In a time when technology is on the rise, concerns for web service security mirror its movement.
Forget about the gold and cryptocurrencies for a moment. The growth of interest in our data, and consequently its theft, is driven largely by data science, machine learning, deep learning, and even business intelligence. The average global cost of data breaches is $4.4 million, according to IBM’s 2025 Cost of Data Breach Report.
If you offer SOAP/REST APIs, cloud apps, or service-oriented architectures, the stakes are even higher. Even a single vulnerability can jeopardize millions of users. This guide explains web services security standards, RESTful web service security essentials, and web services security testing so you can secure web services end-to-end.
With the responsibility of handling extensive personal information about our customers comes the task of managing the currency of data itself in an effective way. This is called web service security and involves a series of preventative best practices as well as monitoring strategies to ensure that sensitive data remains confidential.
Part of hosting a web service is knowing the basics of web service security in order to protect your web application or website. Stay tuned to learn more about it!
Are you ready to start your development project?
We have the developers you need to take your development project in the right direction.
Companies are proven to grow their business faster with Trio.
What Is Web Service Security?
Web service security is the application/API layer of security for SOAP and REST integrations.
These methodologies specifically include detecting, preventing, and responding to cyber threats. Industry standards such as OASIS WS-Security (SOAP), NIST, and OWASP describe both message-level and transport-level protection; for REST, that typically means OAuth2/OIDC, JWT (JWS/JWE), and TLS 1.2+/1.3.
Data protection is crucial to web service security, and there is no better way to illustrate this than the Equifax data breach, which impacted the personal information of approximately 147 million people in September of 2017.
Equifax is one of the three largest consumer credit reporting agencies in the US. It suffered a huge data breach, all because of a little issue that could have been easily fixed.
More on that in a bit. In the wake of their scandal, Equifax will have to pay up to $700 million in fines as part of a settlement with federal authorities over this data breach.
There are many elements to web service security, but knowing the most fundamental parts might help you avoid a future breach and/or more than half a billion dollars in fines.
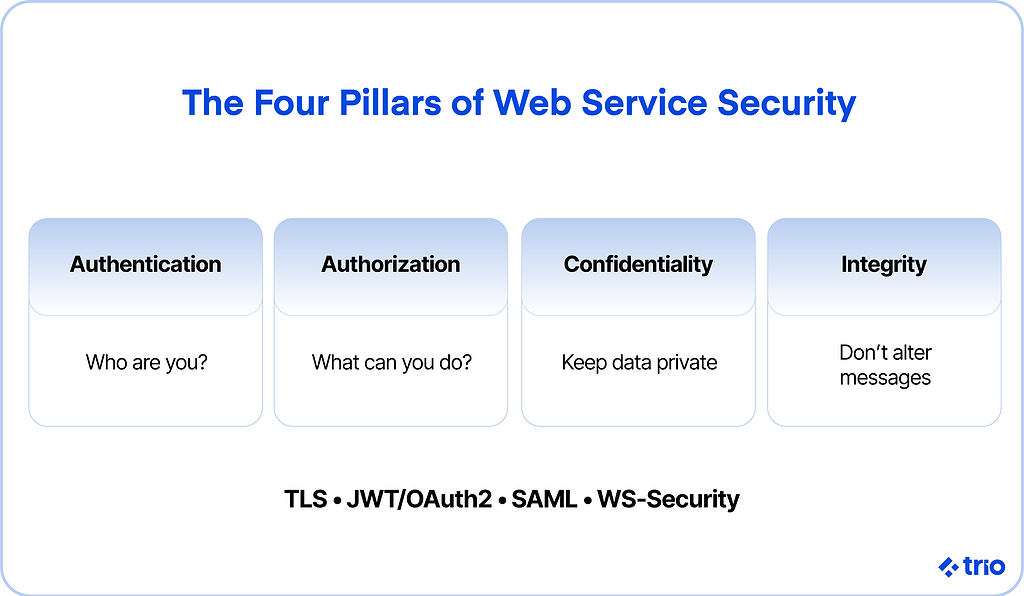
Service-oriented architecture (SOA) security is a security model that addresses a complex combination of services as opposed to only one software program or platform.
Some standards implemented by SOA are explained below.
Authentication
Authentication refers to a means of verification for the user.
Using credentials, a password, or biometrics, or a combo of these methods, a service can verify that the user is who they claim to be.
Authorization
As a form of access control, authorization grants users certain entitlements.
An employee in your tech company, for example, might have access to some directories and programming but not to the same degree as a higher-level employee.
Confidentiality
Confidentiality, or privacy, is the practice of securing data from others.
Personal contact information, for instance, should not be shared with those who can compromise it.
Integrity
Integrity has to do with preventing the alteration of a message. Generally, a sender’s digital signature can certify its validity on one end.
This is closely related to non-repudiation, which ensures that the author of a statement cannot deny its authenticity.
These components of web service security are considered industry standard.
At this point, their implementation is so prevalent as to be considered enforceable web service security requirements.
Any company managing a web service should be aware of these standards and deploy them accordingly through mechanisms like TLS encryption, digital signatures, JSON Web Tokens (JWT), Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML), and OAuth2 authorization frameworks.
Why Do We Need To Protect Our Web Services?
Failing to secure web services can result in serious consequences for the user as well as the service itself.
As an illustration, one coding hosting service was victim to a breach in which an attacker gained unauthorized access to their Amazon Web Services account.
The result of this failure was more than just a fine. The company, called Code Spaces, had to close its shop permanently.
The costs associated with such a web service security blunder, as well as Coding Spaces’s initial disregard for creating an effective recovery plan, proved to be at the root of its detriment.
The hacker had already deleted valuable data and content. This is just one instance of how web security, or a lack thereof, affects a company’s success in dire circumstances.
Unfortunately, failures to keep data safe keep cropping up. In 2023, MOVEit experienced a data breach that exposed the sensitive information of millions of people and thousands of organizations.
All small businesses face the same risk, especially when security budgets are limited and defenses are weaker.
This, of course, does not even begin to scratch the surface of the customers whose information was put in jeopardy in the process.
Successful businesses are built on good reputations and healthy consumer relationships. Ineffective web service security will not garner that effect. They may even result in fines for failing to meet regulatory standards.

Different Web Service Security Standards
Let’s get into the different web service security standards so you can get a better idea of what you need to take into account.
WS-Security
This is what people are usually talking about when they talk about web services security. WS-security is the standard for securing SOAP-based web services and gives guidance on how to apply things like XML encryption and use security tokens like SAML.
As we already talked about, you need to embed security at the message level to ensure things stay confidential, even when you need your messages to go through a bunch of third parties and intermediaries.
Transport Layer Security (TLS)
TLS is something you can’t ignore if you are sending information over the internet in any way.
It makes sure your data stays secure in transit, as the name suggests, so that attackers can’t pick up on any leaks between you and the server, or your client and the server.
You need to use transport-level and message-level security together.
OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect
OAuth 2.0 gives you everything you need to make sure you control access to information, so you only give third parties limited access.
OpenID Connect extends this to make sure you have authentication under control as well, so you can verify the people or entities trying to pass certain access controls.
These two are quickly becoming the standard for securing REST APIs.
SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language)
This is an XML-based framework that lets you exchange authentication and authorization data. If you have never heard of it, it’s not really surprising, since SAML is generally only used in enterprise environments for single sign-on.
It is usually used in organizations where identity management is required, like KYC and AML (Know Your Customer and Anti-Money Laundering) in the financial technology industry.
JWT (JSON Web Tokens)
JWT is a URL-safe token service used for RESTful services.
It is great because of how lightweight it is, making it a good option for stateless authentication in APIs.
SOAP vs. REST Security
We’ve talked about SOAP and REST a couple of times, but what are the differences between the two?
SOAP services rely on WS-Security, and REST services use OAuth2, JWT, and TLS.
For REST APIs, OAuth2/OIDC with least-privilege scopes, short-lived access tokens, JWT (JWS/JWE), CORS policy, CSP, OpenAPI-driven request/response validation at the gateway, mTLS for service-to-service, idempotency keys for writes, and pagination/limits to prevent resource exhaustion.
Both are good options, but the choice will usually depend on whether you are prioritizing enterprise-level complexity, in which case, go with SOAP, or lightweight, API-first architectures.
Use centralized secrets management (e.g., a vault) and cloud KMS/HSM for key generation, storage, rotation, and envelope encryption.
Web Services Security Architecture & Mode
When people talk about a security architecture for web services, they’re really describing how different layers of protection work together.
At the core are identity and access controls, like OAuth2 and OpenID Connect for REST APIs or SAML for enterprise SSO. These decide who can do what, while mutual TLS (mTLS) keeps service-to-service communication trusted.
Then there’s message security, where standards like WS-Security (for SOAP) and JWS/JWE (for JSON-based APIs) make sure your messages can’t be read or altered along the way.
Transport and network layers come next. TLS 1.2+, private subnets, firewalls, and API gateways that help you contain threats before they ever reach the app.
Data protection lives one layer deeper. Encrypt sensitive information at rest using KMS or HSM, rotate keys regularly, and avoid storing what you don’t need.
Finally, round everything out with good observability: structured logs, trace IDs, and real-time alerting so you know when something’s off.
That full stack of identity, encryption, and visibility forms a practical web services security model.
8 Ways to Secure Your Web Service
The idea that web service security is a necessary precaution has been well-established.
Now, if you’re wondering how to secure your web services, pay attention to the eight strategic ways listed below to put cybersecurity at the forefront of your business goals.
1. Don’t Trust Your Client
There is no way of knowing whether our users have good intentions or not.
For a vigilant web service security protocol, we should not trust any data input by our customers. This means that we need to check every input. We can do it with a blacklist or a whitelist.
In a blacklist, we have bad inputs that are deemed unacceptable as user inputs. In a whitelist, we have inputs that we allow to exist. Let’s take a look at an example.
We know that eval() is a function that executes strings as commands in JavaScript.
Surely, a user with good intentions wouldn’t use this kind of content as an email. So, we will replace every eval() with an empty one.

This can be helpful; however, with every new threat, we have to check our code and clean it up.
So for this stage, whitelists are more reliable than blacklists. We have awesome libraries that help us create quick whitelist checks in our routes, such as Hapi/JOI.
Look at this example, where we check the inputs for user authentication:
The example above is awesome because this library will guarantee us two things:
- A good whitelist with good standards. If the input doesn’t fit with our standards, the new Error() will be triggered.
- Protection against Parameter Injection, which means that the hacker tries to send more parameters to our routes. If there exists any different parameter besides email and password, the new Error() will be triggered;
In our example, the only parameters allowed are email and password, and they must adhere to our standards.
Don’t forget to use whitelists, they’re very helpful for web service security! They can help against Parameter Injection and XSS.
2. Use Bind-Params in Your SQL Statements
You’ve probably heard about SQL Injections and how powerful they can be. If you haven’t heard about them, then I suggest you read about them.
In addition, check OWASP Top Ten Attacks. But essentially, an attacker tries to change the queries that the system makes and gets access to the entire database.
I will never forget the day I was talking about SQL Injection breaches with one of my co-workers.
He challenged me to access a system that he made for his friend through an SQL Injection attack.
This system didn’t use the bind params, so I got the admin user, and I put into the password field a well-known SQL Injection command to bypass the password for any user, and voilá! I got admin access.
Now, thinking back to this story, I feel that I should have bet on a beer with him.
The simplest solution is to use bind params. Bind params change the values inside the database, making it impossible to break the query and change to another one.
Nowadays, most ORMs use bind params as the default, but deliberately do not make a custom query and execute it without bind params.
For example, in Node.js + Sequelize, if we want to use a custom query, we could do something like:

The image above shows two methods. The first method is an example with a custom query without bind params, and the second is one with a custom query using bind params.
You might’ve guessed right – the second method is the better one.
If you have to use custom queries, then please don’t forget to use the bind params. Also, ensure that your ORM uses them too.
I know Sequelize does this by watching the logs, and I know the most famous ORMs are using them.
But if you’re the kind of person who loves to try new technologies and libraries, this is a good point to start wondering whether that ORM is good or not.
Therefore, avoid using any kind of query without bind parameters. SQL Injection is considered one of the most famous of the top ten attacks on web applications, and it was discovered in the ’90s.
It shows how negligent most developers and engineers have been.
I still don’t know why we don’t teach developers to use bind params since the first class to connect to the database and make queries.
3. Don’t Expose Sensitive Data
How often does your web service handle sensitive data?
If you have never asked yourself this question, your web service likely exposes more sensitive data than you think.
The first step is to apply an SSL/TLS certificate to our web service and use it as the default connection. We can’t accept HTTP connections anymore for systems that use our personal information!
This certificate ensures that we have an encrypted connection between servers and customers, which almost mitigates “data sniffing” from a third party. This prevents a man-in-the-middle attack.
Next, ask yourself: How are you helping hackers access your information?
By showing system errors to them!
Errors can sometimes display a lot of sensitive information, such as the database system, table names, field names, constraint names, programming languages, and more.
Sometimes we can even see hosting information and passwords. When that happens, it gives hackers a means of exploring the known security breaches for the technology, systems, frameworks, and programming languages that your web service works with.
I can’t stress this one point enough. Do not show errors to users.
We need to intercept them and send them to programs like Rollbar or Sentry. These programs offer excellent support for a wide range of languages.
Not to mention, it’s pretty simple to configure your exceptions to show a default message to the user and send the system error to those tracker programs.
Altogether, it’s best to show the user a default error message or a descriptive, user-friendly error message instead of showing the whole system error.
A great example of a default error message is “Internal Server Error”. It’s much safer for a system to show this rather than the whole system error.
4. Check Your Third-Party Libraries
I mentioned before that Equifax will pay up to $700 million in fines. Could you imagine your company being responsible for a huge data breach like that?
So, what happened with Equifax? Well, it’s not a complicated story to tell.
Equifax had a system that used Apache Struts. Two months before the attack, Apache Struts had announced a new patch to fix a specific vulnerability.
Two months later, the hacker was exploiting this vulnerability, meaning that Equifax didn’t update its systems.
This was the result:
To prevent this kind of problem, we need to examine our third-party libraries. Nowadays, it’s almost impossible to create any application without using any third-party library or framework.
But one has to ask, who made that library? How well managed is it?
We are human beings, and we make mistakes. Therefore, as a developer, it is your responsibility to manage the integrations you use.
This means assessing their risks, understanding the potential effects they can have on your system, and staying up to date on any updates.
There’s a fantastic tool called Snyk, which keeps developers alert to failures, vulnerabilities, and problems with your integrations.
Snyk has a huge database with a lot of contributors, and when they find a new vulnerability, they warn all their customers who use Snyk in their applications.
Most of the time, they fix the new vulnerabilities automatically with one command that you need to run. Also, Snyk warns you via email.
Snyk is a truly incredible tool when it comes to web service security! Along with Dependabot and GitHub Advanced Security, these tools can automatically scan dependencies, notify you of vulnerabilities, and sometimes even patch them.

I personally appreciate how companies are working hard to provide consumers with outstanding value, particularly in terms of security.
That’s why their valuation surpasses one billion dollars.
They also have free plans and paid plans. Currently, I use the free plan for my personal projects. They support many languages and package managers.
5. Set Limits for the User
I’m very enthusiastic about cryptocurrencies, particularly Bitcoin, and I discuss the applications of blockchain technology on Trio’s blog.
I remember witnessing the exchange falling because Bitcoin’s price was rising too fast.
After the owner lost a lot of money, they decided to invest more in architecture and introduced a new feature to their APIs: limits for the client.
In the exchange, to guarantee good performance, they send a new result every minute. If you request the same route multiple times within the same minute, you’ll get the same cached result.
It’s a great way to ensure more performance and to decrease the chances of your server going down.
Of course, we have to study and analyze the business impacts of caching the response every minute.
Using a layer to protect your service from DDoS attacks, such as Cloudflare, is also a great idea, and we can combine their solution with a good architecture on our APIs.
This is actually what the exchange did. They combined a cached result with Cloudflare DDoS protection.
You can use an API gateway to enforce quotas, apply caching for predictable responses, and configure burst limits for abusive traffic.
6. Read the Security Section in the Manual of Your Library
Apparently, we are reading less and less, generation after generation. Also, we’re having problems paying attention for extended periods of time.
As a software engineer, I know that patience, attention, and reading are big facets of our daily routine.
Ergo, it’s vital that we discipline ourselves and read the documentation from our frameworks and third-party libraries, including the security section.
By using Express, I’ve noticed that we have a section called “Advanced Topics” and “Security Best Practices”.

This is awesome.
But I know that most software engineers who have installed Express haven’t read the Express documentation and probably never bothered diving into the “Advanced Topics” section, much less the “Security Best Practices” page.
Reading is probably the easiest way to familiarize yourself with the base tenets of web service security.
To my surprise, when I decided to implement Express in one of my APIs, I saw this section and found that Express offers wonderful documentation on how to protect your web service with Express.
With that documentation, I was able to learn how to use Express in a way that did not compromise my system in the future.
7. Don’t Be Paranoid and Continue to Study Security
After studying security for my applications and web services, I started to go a little crazy!
I couldn’t finish my tasks on time because I was preoccupied with potential security breaches in my code.
We have to remember that even big organizations like the CIA, Sony, eBay, Yahoo, JP Morgan Chase, Netshoes, Dropbox, and YouTube have been hacked.
Considering that, don’t be so paranoid about your services. After all, if hackers really want to hack your application, they will likely find a way.
It’s just in their nature. The real question is: how much time do you need to identify that a hacker bypassed your security barriers?
With good logs and a strong alert strategy, we can identify breaches sooner and thus act on them quickly.
This isn’t an excuse to think it’s pointless, because hackers will win.
Developers and cybersecurity professionals work to build as many walls, mazes, traps, and other defenses for hackers to become discouraged and leave their system alone.
So it’s best to make the hacker’s job as difficult as possible in the hope that they will move on to their next target.
Also, don’t neglect to study web service security. This article covers the most basic web service security techniques.
However, we should be learning these approaches in college or in beginner tutorials on the Internet. Most developers are not interested in protecting their services at a basic level.
That’s a problem.
Again, don’t be consumed with paranoia. At the same time, continue to study and invest time in protecting your applications.
A good resource to study is the OWASP page, especially the projects page. You can download the “Lab” projects and attempt to hack the software yourself.
These projects have security breaches implemented on purpose. It’s fun to learn in this way, where you’re in the position of the hacker, and the software engineer is trying to stop your attack.
This form of web services security testing is similar to a coding challenge. The Node.js project OWASP learning environment is called NodeGoat. There’s a tutorial guide to help you hack and protect the project.
There are projects in other programming languages as well. It’s worth taking a look at them.
The only way to truly find ways to stop a hacker is to think like one and break your own system. This is the fundamental idea of penetration testing, which is a major player in web service security.
8. Logs and Monitoring
There are some situations where we need to audit our data to answer questions like “Who edited this line?” or “What’s making our server so slow?
These are key questions to ask regarding web service security.
We can’t answer these questions without good logs. That could be dangerous to any company, especially when it needs to identify a user with bad intentions.
Imagine the following situation:
Someone hacked your web service to process payments from the clients. And your boss asks, “How did the hacker pass through our security barriers?”
This could be a tough question if you don’t have good logs to start your investigation with.
I doubt any executive is trying to hear that there weren’t any logs, and therefore, there is no way of knowing.
That wouldn’t get you very far. Remember to keep logs and ensure you have a system in place to track them.
These are only a few of the strategies you can use to ensure that your web service is secure.
As mentioned, you should take the time to do your own research and study up on best practices for web service security.

Elevate Your Team with Trio AI Talent
Empower Your Projects with Trio’s Elite Tech Teams
Conclusion
It’s important to start thinking about cybersecurity with our web applications and applying what we learn through research and practice to guarantee a safer system.
Equifax and Code Spaces are good examples of what not to do.
You can use the intel provided here to avoid those mistakes. This includes utilizing better coding techniques like bind-params or even making use of third-party services like Snyk.
If you want to guarantee your system is secure, it would be in your best interest to hire skilled developers to enhance your cybersecurity measures.
At Trio, we offer remote software developers who can work cohesively with your company and business goals.
Hopefully, we’ve convinced you that web service security is one of them.
Trio bridges the gap between software expertise and South American developer talent. Meet our top-tier Argentine, Chilean, and Brazilian developers for outsourcing excellence.
Contact Trio now to get the security you need.
FAQs
What is web service security?
Web service security is the protection of SOAP and REST APIs through authentication, encryption, and monitoring at both the transport (TLS) and message layers.
What are web services security standards?
Web services security standards include WS-Security for SOAP, OAuth2/OIDC and JWT for REST, SAML for SSO, plus TLS and key HTTP security headers.
How do I secure a web service?
To secure a web service, enforce TLS 1.2+, use OAuth2 scopes, validate inputs, enable WAF protection, vault secrets, and monitor logs for anomalies.
What is web services security testing?
Web services security testing combines static, dynamic, and dependency scans with API penetration testing based on OWASP ASVS and API Top 10.
How can I protect services using WAF security measures?
Protect services with WAF rules that block OWASP Top 10 attacks, add rate limiting and bot mitigation, and send logs to your monitoring system.






