If you work in payments or fintech, you already know that data security is not an optional feature. Card data, encryption keys, and payment tokens move constantly across networks and applications, and attackers only need one weak link to cause real damage.
For many organizations, the solution used to be simple. You put a payment HSM in your data center and tightly controlled who could touch it.
Today, the reality looks different.
Cloud payment systems, global users, and fast-moving digital products have changed what security needs to look like. Cloud HSM services now offer the same tamper-resistant cryptographic protection without the heavy on-premises footprint.

If you are evaluating these systems or planning a migration, the details in this guide will help you understand where a cloud HSM fits, how tokenization works with HSMs, and how teams approach deployment in real payment environments.
At Trio, our fintech software engineers often work with payment service providers and fintech teams that are modernizing systems like this, helping organizations balance security and flexibility as they scale.
Understanding Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) in Payments
If we strip the concept down to the basics, an HSM is a hardware device that is used to protect encryption keys and perform cryptographic operations securely.
In the payment industry, that means keeping card data and PINs safe, enforcing PCI DSS controls, and ensuring that sensitive data stays protected even if other systems fail.
What Is a Hardware Security Module?
A hardware security module is a tamper-resistant system that generates, stores, and uses encryption keys without exposing them to software or memory.
You can think of it as a locked vault for cryptographic key material. Keys never leave, and every operation is tightly verified.
Core Functions: Encryption, Key Management, and Authentication
HSMs encrypt data, sign transactions, generate digital signatures, and manage the entire lifecycle of cryptographic keys.
They also authenticate sensitive requests so only approved systems can access payment information.
In practice, this means secure PIN processing, EMV validation, and encrypted card transactions across payment systems.
Tamper Resistance, FIPS Validation, and PCI Requirements
Payment HSMs are physically secured to prevent tampering, drilling, or probing.
Many operate at certifications like FIPS 140-2 or FIPS 140-3. For card environments, PCI PIN and PCI PTS apply, and some systems require FIPS 140-2 Level 3.
These standards exist because the payment card industry depends on repeatable, audited, hardware-enforced trust. A well-designed HSM architecture is simply part of the foundation of compliance and payment security.
Types of HSM Deployment: On-Premises vs Cloud HSM Options
Organizations often find themselves navigating both traditional on-premises HSMs and cloud HSM platforms as they evolve.
Traditional On-Premises HSM Appliances
On-premises HSMs offer full control and direct access to the HSM.
They live in your data center, and you manage everything.
Some large banks still prefer this because it feels predictable, and their compliance model was built around it.
The trade-off is the effort required to provision hardware, maintain firmware, support high availability, and scale manually.
Cloud HSM Services
Cloud HSM solutions provide similar dedicated hardware security boundaries, but as a managed service inside a public cloud.
AWS CloudHSM and Azure Payment HSM are well-known examples.
The cloud service provider handles physical security, infrastructure resilience, and scaling.
You still control the cryptographic keys, which helps satisfy security and compliance needs without the need for heavy hardware investment.
Hybrid Deployment Models in Financial Environments
A hybrid model mixes on-premises HSMs and cloud HSMs. It appears to be the most common path lately, especially for payment applications that are being modernized gradually.
We have noticed clients running vaultless tokenization in the cloud while still keeping EMV and PIN security workloads on-prem until they feel ready to shift.
Why HSMs Matter in Payment Security
Payment environments need strict control of cryptographic key access, PCI DSS compliance, and reliable enforcement of payment security standards.
Securing Cardholder Data and PIN Protection
HSMs protect Primary Account Numbers, encrypt PINs, and ensure sensitive data is only handled inside secure environments.
When attackers target payment systems, they often look for weak key management processes or exposed cryptographic keys. With an HSM enforcing access, that risk drops significantly.
Tokenization and Protecting PANs
Tokenization replaces real card numbers with tokens.
If an attacker intercepts the token, it is not useful.
An HSM supports token generation and key storage, and in vaultless tokenization systems, it can create tokens mathematically without storing sensitive card data.
Tokenization can streamline compliance efforts because it keeps raw PANs out of most systems.
Meeting PCI DSS and EMV Controls
If you work with payment data, PCI DSS applies.
Regulations like PCI P2PE, PCI HSM, and EMV rules govern how keys must be handled.
HSMs ensure encryption keys stay secure and that cryptography follows strict policy. Payment HSMs really are the heart of compliance in card networks.
Fraud Prevention in Real-Time Payments
Modern payment processing moves fast. HSMs help verify transactions, authenticate requests, and enforce security rules without slowing the experience.
It may sound technical, but it is what allows card networks to approve or decline payment transactions in milliseconds.
Cloud HSM Platforms and Payment Capabilities
Cloud HSMs give you security infrastructure without needing to install a device in your own rack.
Here is what the major cloud service providers offer.
AWS CloudHSM
AWS CloudHSM provides dedicated HSM capacity with full control of your cryptographic keys.
It integrates with AWS services, supports asymmetric encryption, and can work alongside AWS KMS for layered security.
For teams running large payment workloads, AWS often becomes appealing because the cloud offers global presence and high availability by design.
Azure Payment HSM
Azure Payment HSM focuses on card processing and payment security.
It supports dedicated payment workloads and is commonly adopted by processors and service providers moving legacy systems forward.
You still control key management, but the heavy infrastructure work is handled for you.
Google Cloud and Third-Party Payment HSMs
Google Cloud offers a cloud hardware security module service, and some teams choose providers like Thales, Utimaco, Futurex VirtuCrypt, or Entrust nShield as a Service for payment applications.
These providers often specialize in PCI workloads or offer additional geographic coverage that matters for international payments.
Cloud vs On-Prem Payment HSMs
This choice usually comes down to your operating model.
On-premises HSMs give full control and satisfy long-standing risk policies. Cloud HSM solutions allow rapid provision of capacity, easier scaling, and smoother deployment.
Most organizations end up blending both, especially for multi-cloud tokenization strategies.
At Trio, our team of fintech developers has supported clients moving from local payment data centers to hybrid payment HSM infrastructure.
Teams usually start with tokenization and vault modernization because those areas deliver visible efficiency gains.
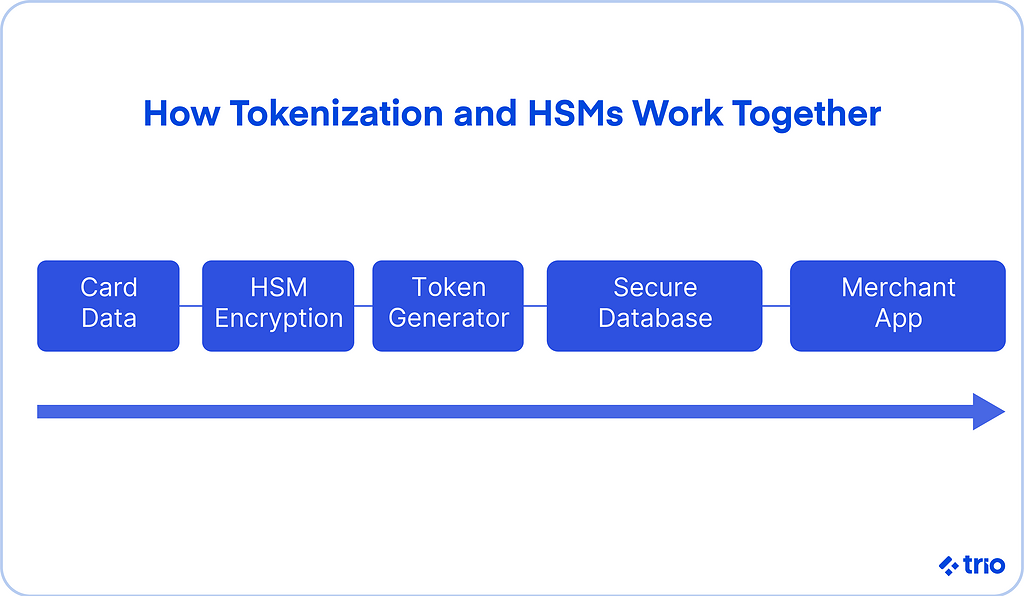
Payment HSM Use Cases and Tokenization Workflows
HSMs power more than simple encryption. Payment systems depend on them for key management, card security, and secure tokenization.
Encrypting Data and Securing Transactions
Payment HSMs encrypt sensitive data at rest and in transit and ensure cryptographic requests are verified. This includes EMV processing and PCI P2PE workflows.
When a card is scanned or tapped, the encryption keys and secure digital signatures behind that process rely on an HSM.
Key Management and Tokenization in the Cloud
Cloud HSMS supports advanced key management, including key rotation and lifecycle tracking across environments. Key management becomes especially important in multi-cloud systems.
Without a structured approach to cryptographic keys, compliance breaks quickly, and sensitive data may be at risk.
Vaultless Tokenization for Scale
Vaultless tokenization creates payment tokens without storing them. It uses cryptographic algorithms inside the HSM to derive tokens deterministically.
This reduces lookup overhead, improves latency, and keeps payment data safe.
It is likely to become the default approach for cloud-based payment processing applications.
Deploying Cloud HSMs and Migration Guidance
Moving to a cloud HSM model takes some planning, but the benefits outweigh the complexity for most teams.
Planning and Deployment Steps
You will need to plan your cryptographic key import, provision your HSM cluster, configure security roles, and verify integration with your identity system.
You may migrate keys or generate new ones.
Teams often take a phased approach to reduce risk and maintain compliance controls.
Best Practices for Cloud HSM Adoption
Least privilege access is important.
Rotate keys regularly, audit cryptographic key use, and feed logs into a SIEM to spot anomalies.
If you work in payments, meeting compliance standards like PCI DSS and PCI PIN is not optional.
Keeping documentation clear makes audits much easier later.
Challenges and Common Trade-offs
Latency can surface during busy periods, and vendor lock-in may matter if you expect to run payment workloads across more than one cloud.
We’ve also found that legacy systems sometimes need middleware. That said, most organizations adapt successfully. As long as you go in with clear architecture goals, challenges tend to be manageable.
Choosing Payment HSM Vendors and Evaluating Solutions
With multiple cloud HSM platforms and traditional vendors available, selecting the right path may take some reflection.
What to Look For
Review security certifications, available regions, API capabilities, and support for payment key management workflows.
Teams also evaluate HSM management tools, operational overhead, and how well a vendor fits hybrid models if your security requirements include sovereign cloud or strict physical security access.
Leading Vendors
Thales, Utimaco, Futurex, AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud appear frequently in enterprise environments.
Some teams prefer general-purpose HSMs for mixed workloads. Others choose dedicated payment HSMs because they are built for PCI environments.
Payment HSM vs General Purpose HSM
Payment HSMs follow PCI PTS and PCI HSM standards and specialize in card security.
General-purpose HSMs support broader cryptography.
When speed matters, look at transactions per second and latency benchmarks.
We have helped clients benchmark performance across vendors and clouds and found that workload patterns influence the choice as much as vendor features.
Future Trends in Cloud HSM and Payment Cryptography
The payment security landscape rarely sits still, and although we can’t predict the future, we can look at some of the current trends to point us in the right direction.
Cloud-Native Cryptography and Keyless Models
Cloud payment systems are shifting toward centralized cryptographic services and API-first workflows.
Keyless encryption and shared responsibility models reduce key exposure risk.
Multi-Cloud Federation
Teams want crypto controls that work across major cloud providers.
Cloud and on-premises HSMs will likely continue to coexist, although with more unified management.
AI-Driven Anomaly Monitoring
AI may help detect unusual cryptographic use faster than traditional rule-based systems.
This could be useful for spotting key abuse or payment fraud signals.
Preparing for Post-Quantum Cryptography
Quantum-resistant algorithms are coming.
Updating HSMs and cryptography stacks will take time, so gradual planning helps avoid rushed changes later.

Conclusion
Cloud HSM adoption in the payment industry is not a theoretical trend. It is happening because organizations want secure cryptography without the friction of legacy infrastructure.
Whether you stay on-premises, use cloud HSMs, or mix both, placing controls around cryptographic keys is still the foundation of data security. The right architecture gives you agility and security at the same time.
If you ever want outside help mapping your HSM strategy, exploring cloud payment HSM options, or evaluating tokenization models, the team at Trio brings experience from multiple payment security projects.
We have seen the benefits and the challenges up close, and we believe thoughtful planning makes all the difference.
To hire expert fintech developers for your project, get in touch!
FAQs
What is a payment HSM?
A payment HSM is a hardware security module designed for card networks and banking systems, and a payment HSM protects cryptographic keys and handles secure PIN, card, and token transactions under PCI standards.
How does cloud HSM differ from on-premises HSM?
Cloud HSM differs from on-premises HSM by providing dedicated cryptographic hardware as a managed service, while on-premises HSM requires physical deployment and full in-house management.
Why do payment systems need HSMs?
Payment systems need HSMs because payment systems rely on secure key storage, PIN processing, and card encryption to meet PCI DSS and protect sensitive data from compromise.
What is vaultless tokenization?
Vaultless tokenization is a cryptographic method for generating tokens without a central token vault, and vaultless tokenization improves scalability and reduces sensitive data storage.
Is Cloud HSM PCI compliant?
Cloud HSM is PCI compliant when using a validated payment HSM service and proper key management because cloud HSM must meet PCI DSS and PCI PIN controls for financial data security.
Can you use HSMs in multi-cloud environments?
Yes, you can use HSMs in multi-cloud environments, and you can use HSMs across clouds by federating keys or running hybrid on-premises HSM and cloud HSM clusters.
What key management tasks does an HSM handle?
Key management tasks an HSM handles include generating, rotating, storing, and retiring cryptographic keys to ensure encryption keys never leave secure hardware.




