With the mobile market continuing to grow exponentially and the demand for applications exploding, the business of app creation has never been more attractive.
The mobile app economy continues to surge, drawing more entrepreneurs and product teams than ever. But the real question for you is: how do you create a mobile app that actually succeeds?
Building a mobile app requires an abundance of patience, clever financial investments, and a relevant technical skill set provided by qualified developers. This updated guide walks you through the process step by step so you can move from idea to launch with confidence. Read on to learn more!
At Trio, we deliver top-tier content and insights in software development, and also offer top-tier South American developers for outsourcing. Discover how our talented Argentine, Chilean, and Brazilian developers can elevate your projects today.
If you’re ready to start your development project, we can match you with the right talent and help you move faster.
Are you ready to start your development project?
We have the developers you need to take your development project in the right direction.
Companies are proven to grow their business faster with Trio.
What Is a Mobile App?
A mobile app is a software application specifically designed to run on mobile devices like a phone or tablet. WhatsApp, Facebook, and Subway Surfers are currently among the most popular mobile apps.
The original purpose of apps was to facilitate productivity. Calendar, email, and contact list apps were once the norm. Now, these come built-in in any typical smartphone.
But demand nowadays revolves around mobile game apps, GPS services, food delivery, and other services that cater to the basic convenience and entertainment needs of smartphone users.
The word ‘app’ came into use with the rise in popularity of mobile applications. It was voted word of the year in 2010 by the American Dialect Society.
Apps span every industry: from short-form video platforms like TikTok, to AI-powered learning tools like Duolingo Max, to mobility services like Uber. Modern apps aren’t just about convenience. They’ve become the primary channel where users shop, learn, play, and manage daily life.
3 Types of Mobile Apps
The nitty-gritty, software side of mobile apps recognizes three different modes of mobile app development – native, cross-platform, and hybrid.
Native Apps
Native app development involves the process of building mobile apps that are only compatible with one platform. Such specificity allows software engineers to develop apps that are noticeably high-performing and high-functioning.
Since developers know precisely what platform their app will be released on, they have far-reaching access to targeted features and functionality.
For developers building mobile apps for iOS, XCode is an integrated development environment (IDE) for Apple operating systems where programmers can write and test their apps in Swift or Objective-C.
For developers building mobile apps for Android, code in Java or Kotlin, Android’s respective IDE is Android Studio.
Tools like SwiftUI for iOS and Jetpack Compose for Android are making native development faster and more expressive, while still delivering best-in-class performance.
Cross-Platform Apps
Cross-platform apps are made to be compatible with multiple mobile operating systems.
React Native, Xamarin, and Flutter are standard software tools for developing cross-platform apps.
While it is easier to take the cross-platform development route to release your app in a broader network, performance is not expected to be on par with native apps. Customization is also more difficult.
Flutter, in particular, has become one of the leading frameworks, praised for its near-native performance and strong community support.
Hybrid Apps
Hybrid apps use traditional web technologies like JavaScript, HTML, and CSS, but encapsulate the product into an application that’s optimized for mobile users. This is less demanding in terms of cost and time for developers and businesses.
There is some confusion in the industry about the difference between hybrid apps and cross-platform apps.
It’s important to note that hybrid apps rely on web development techniques but deploy in a mobile environment.
As an aside, progressive web apps (PWAs) share some similarities with hybrid apps. They are built with web technologies but run in a browser, and no installation is required.
PWAs replicate the speed of a mobile app, despite not offering much more interactivity than a typical website.
The Ionic framework is a popular developer tool for building both hybrid apps and PWAs.
Direct Comparison: Hybrid vs Cross-Platform vs Native App Development
| App Type | Cost | Performance | Best For | Example Tools |
| Native | Higher | Excellent | Apps needing speed & advanced features | SwiftUI, Jetpack Compose |
| Cross-Platform | Medium | Very Good | Startups targeting iOS + Android | Flutter, React Native |
| Hybrid/PWA | Lower | Moderate | Budget-friendly, content-driven apps | Ionic, Angular, Vue |
Why Develop a Mobile App?
Mobile apps are, by definition, mobile. This inherent convenience and flexibility can attract a significantly larger number of consumers to your product or service than otherwise.
But in a more general sense, a mobile app can grant you flexibility in your industry market. Developing a mobile app can allow you to expand your business.
In public relations, you’ll have the chance to gain a media presence and appear on lists for recommended apps. You’ll also be able to compete in the same market as your competitors.
The competition likely already has an app to offer its consumer base. And if not, you can be ahead of the game.
Needless to say, you can make money off mobile apps, too. You have the option of putting your app on the app store with a price tag. Alternatively, you can explore other strategies for boosting capital from mobile apps, as discussed later.
And it seems the stakes are only getting higher. Consumers now spend more than 4.5 hours per day on their phones, and global mobile ad spending was projected to surpass $400 billion in 2025.
Having a well-designed app is increasingly the main way businesses reach, engage, and retain their audiences.
5 Advantages of Developing a Mobile App
Many businesses believe they are doing just fine because they have a website, and they feel this can achieve the same results. But mobile apps are a whole different ball game.
1. Accessibility
Apps are faster than websites. They’re quicker to access, and the performance is unparalleled as well. Not to mention, with a mobile app, users have online and offline access, as some elements can be stored in cache or downloaded for offline use.
This ensures users can still engage with core features without a constant internet connection.
2. New Consumer Base
Mobile apps tend to garner a younger fan base. In 2017, people aged 18-24 spent two-thirds of their time on smartphone apps. While Boomers may shun them for their behavior, you can use this new form of consumption to your advantage.
Gen Z and Millennials remain the heaviest app users, but adoption among Gen X and Boomers has risen sharply thanks to fintech, health, and lifestyle apps, meaning your potential audience is broader than ever.
3. Engagement
On a mobile app, you’ll see engagement in two ways. First, you’ll see an increase in engagement in your product due to new consumers. But you’ll also see a larger engagement in the context of consumer-to-business (C2B) interactions.
Customers are more likely to leave feedback about your product or the app itself through the app store or through a ‘Contact Us’ segment of your app.
Engagement also comes through push notifications, in-app chat, and gamified features that keep users active over time.
4. Personalization
Mobile app developers can give smartphone users more personalized experiences. Instead of seeing what everyone else sees on a website, you can use features like Dashboard or Recent History tabs so the experience can be catered to the user.
AI and machine learning now enable hyper-personalization, tailoring recommendations, offers, and app flows to individual user behavior in real time.
5. SEO Ranking
Search engine optimization (SEO) plays a part in the app store as well. Both your in-app content and the app itself can be optimized for higher rankings. Naturally, your business will do better the higher it ranks.
This is now referred to as App Store Optimization (ASO). Just like websites compete for Google rankings, apps compete for visibility in the App Store and Google Play.
5 Steps To Begin Developing
Unfortunately, many business-oriented minds become too eager about developing a mobile app and forget the basics. Before you begin to build your mobile app, there are a few steps to account for.
Think of these as your foundation.
These steps can be accelerated by AI tools, rapid prototyping frameworks, and lean startup practices, but the fundamentals remain the same.
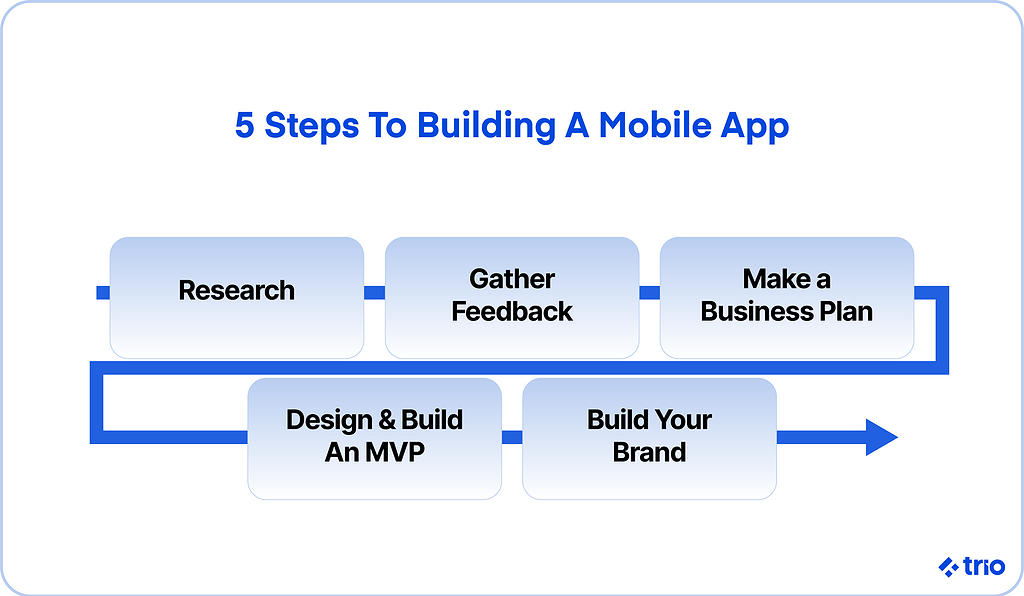
1. Research
There is a massive problem with overconfidence amongst entrepreneurs in the app industry. To a beginner, making a significant profit seems far more straightforward on paper than it actually is.
Too many app creators overlook the most crucial aspect of app validation – the research.
Researching your app’s subject matter is critical. Without understanding your market, the potential risks, and the optimal strategy for your target demographic, your chances of success are far lower than you might think.
Today’s app market is highly saturated. Most of your original ideas are not exactly original.
But competition doesn’t have to be negative. Like any other creative pursuit, you can add an interesting twist or spin to make your app unique.
This is why it is essential to research the past, present, and future of your app’s market. The most successful entrepreneurs seek to understand their markets on a deep level.
A well-researched and nuanced comprehension of your subject matter will lead to better-developed ideas.
Use tools like Statista, Google Trends, and AI-driven market research platforms to validate your idea quickly and identify emerging niches.
2. Seek feedback
Once you have an understanding of your app’s market, it’s time to seek out feedback. You’ll benefit from collecting as much information as possible in the form of feedback.
Gather as many opinions as possible, and you will have far more accurate data to assess the feasibility of your project.
Don’t look for empty compliments or a ‘yes man’. You need real, honest feedback. Give value to critical opinions and try to remain objective. Your ego does not belong in the feedback process.
The more you learn, the better you’ll become. As your success grows, your confidence will too.
In effect, you will experience less emotional distress when your ideas are criticized, and your situational intelligence will rise.
Consider releasing a quick no-code prototype (via Bubble, Glide, or Figma mockups) to gather real user feedback before committing heavy resources.
3. Make a Business Plan
Get to know your potential clients. Even with a fleshed-out business plan, without customers, your business is nothing.
Human-centered design and development processes result in better product reception by the market and more engagement from the end-user.
Keep in mind that app development doesn’t stop when the code is written. It encompasses all related processes, from tech support to promotion, which should also be included in your business plan.
A balance of your business goals and customer needs should be reflected in your business plan when you are forecasting profits and setting the breakeven point.
It’s best to have at least three forecasts – one realistic, one negative, and one positive – to have an accurate demonstration of potential business risks.
Support your financial plan with a marketing and sales strategy that will illustrate who your customers are, how they can be reached, and how you can keep them engaged with your app for extended periods. This will secure a steady return on investment (ROI).
Take your business plan seriously and be prepared to show it to investors, partners, and other stakeholders.
Don’t forget to include a retention strategy (push notifications, loyalty programs, in-app personalization) in your plan. Investors now expect to see not just acquisition costs, but lifetime value models.
4. Build an MVP
A minimum viable product (MVP) is a version of your software that contains only the key features of your app.
The MVP allows developers to present their ideas early on so they can start collecting feedback.
It is imperative in learning how your customers will interact with the app. More importantly, developing an MVP will help you determine whether your app will be profitable in the first place. Ultimately, your MVP will mitigate any risk-taking.
Given that the launch of your MVP is successful, you can start looking into companies that might be interested in developing your application.
Be selective in your decision-making. Once you choose your developers, be clear about your requirements and firm about your budget. Ask all the questions you need.
MVPs are often built with cross-platform frameworks like Flutter or React Native to minimize costs while maximizing reach. AI-assisted development (e.g., GitHub Copilot, ChatGPT-based coding) can also accelerate prototyping significantly.
5. Build Your Brand
It’s never too early to start building your brand. And once your app is released, this should become an even bigger priority.
Your image and brand must capture the essence of your app’s purpose.
Effective visual identity and design go a long way towards promoting interest and awareness in your app.
If your app isn’t attractive and easy to use, people won’t give it the attention it needs to grow. So keep aesthetics in mind; they can make or break your app.
Branding also means creating your app’s presence on social media before launch, setting up an App Store preview page, and building an email waitlist to generate buzz.
Stages of Mobile App Development
Now that you’re finally ready to start building your app, you’re probably wondering what actually goes on in the development process.
Several stages of development must take place for you to build your mobile app successfully.
The stages of the mobile app development process cannot be separated from one another and are tightly connected.
Each stage of development takes a different amount of time, but with experienced developers, your whole project should take between three and six months.
The success of your project depends on how well the foundation for development is laid, including how clear you were about your app’s requirements. Here’s a breakdown of what to expect.
Most teams follow Agile or Scrum methodologies, meaning these stages are iterative and may overlap. Continuous integration/continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines are also standard, allowing you to release updates faster and more reliably.
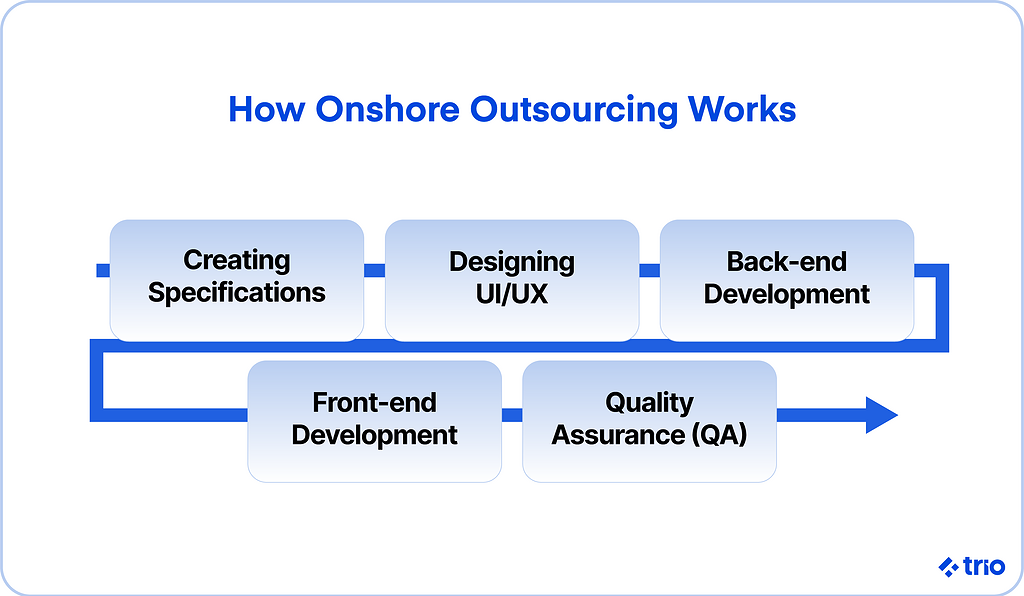
Specifications
Specifications, or specs for short, take about 10% of the whole application development process.
At this step, you’ll be focusing on the app’s functionality, navigation, features, and other technical details.
This means vague ideas about the final product must be further developed and/or replaced with as many specific details as possible.
Modern tools like Jira, Notion, and Miro are widely used to collaborate on specifications and user stories. Clear, written documentation remains the bedrock of success.
UI/UX
User interface (UI) and user experience (UX) play a crucial role in the project’s success.
They address both the visual appearance of the application and how end-users will interact with your product.
This stage of mobile app development typically accounts for 20% of the total development time.
UI/UX is often designed in Figma or Sketch, with interactive prototypes tested on real devices. Accessibility and inclusivity are also non-negotiables.
Back-End Development
Back-end development takes care of all the internal structures that you will need to support your application, like application programming interfaces (APIs), data diagrams, servers, data integration, and push notification services.
However, for relatively simple apps, you may want to use a back-end as a service (BaaS) platform.
BaaS providers provide all the necessary technology to structure your app. In essence, these providers allow you to outsource this part of development entirely, saving you time and resources.
Popular backend options include Firebase, Supabase, and AWS Amplify.
Front-End Development
Front-end development focuses on the client-side of the application, handling everything the user sees on the screen.
You must ensure the user has a seamless experience and interaction. This end of development relies heavily on the information provided by UI and UX designs.
While custom back-end development can be substituted with BaaS platforms, front-end development is where doing your due diligence really pays off.
Cross-platform frameworks (Flutter, React Native) are increasingly used to handle front-end across iOS and Android with a single codebase. This accelerates time-to-market while still delivering near-native quality.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance (QA) is a means of verifying that your application is up to standard. This stage in particular is intertwined with back-end and front-end development.
Thus, it takes approximately 60-70% of the whole development process. Software quality assurance addresses particular criteria that, if followed, guarantee a high-quality software product.
Testing is equally essential and exists as an ongoing process during development, where you can detect minor errors in functionality and fix them before the application’s release.
As expected, this will lead to more genuine feedback and prevent unexpected problems when you finally launch your product on the market.
Automated testing (using Cypress, Appium, or Detox) is the norm these days, complemented by manual exploratory testing. Many teams integrate QA directly into their CI/CD pipelines for faster release cycles.
Design Thinking in the Mobile App Development Process
Intentional design, functionality, optimization, and user-friendly features are the building blocks of a quality software product.
To ensure your product is well-liked by its users, you need to put yourself in their shoes.
One way to do this is through design thinking. Design thinking prioritizes empathy. In other words, don’t assume what your customers want. Let them tell you. And listen.
There are various academic explanations of what design thinking is, but to put it simply, it is a creative process of human-centered problem-solving.
While it might seem like this was always the goal of software development, this is not the case.
Software is built for people, but traditional development only targets the logical side of the building, where behavior is optimized.
But humans tend to be more emotional than an assortment of clicks and buttons can really convey. You need to dig deeper into their motivations and feelings to truly improve your productivity.
Businesses research to observe how users interact with their products. They ask questions about specific features to determine what works and what doesn’t. Online forums like Reddit can also be helpful for secondary research.
When Swiss houseware company Zyliss wanted to design a new set of handy kitchen tools, a team of designers spent time with people in the kitchen. They noticed that some people licked their spoons before placing them in the sink.
None of the questionnaires took note of this behavior, yet the team saw a less obvious need and addressed it with their design: “mouth-friendly” scoops.
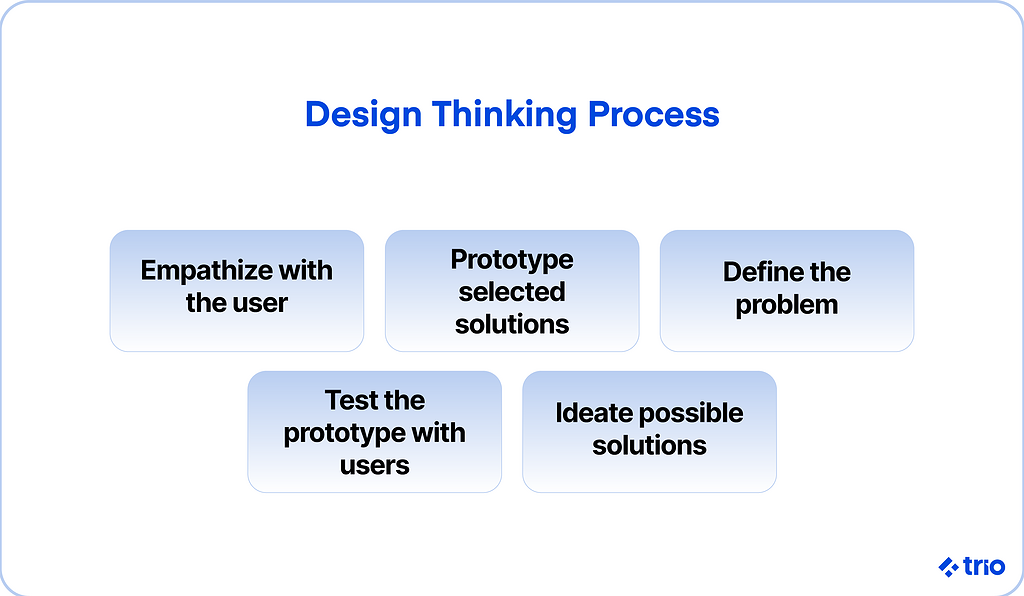
Design Thinking Process
The design thinking process consists of five non-linear steps. You can jump from one to the other to make adjustments:
- Empathize with the user. Software engineers can gain a deeper understanding of how to improve their product by listening to user feedback and identifying pain points. Pain points are specific problems that prospective customers may experience.
- Define the problem. Engineers should identify a problem by analyzing gathered information through a human-centered lens. The goal of solving the problem will guide the next steps of the development process.
- Ideate possible solutions. This is where the team brainstorms. There are plenty of techniques from the Worst Possible Idea to Mind Mapping. The purpose of this step is to initiate the creative process and explore new solutions.
- Prototype selected solutions. Once you choose the most practical ideas, the prototyping stage begins. You can test multiple ideas, and each prototype should give you a better idea of how to manage the functionality and user experience of your app.
- Test the prototype with users. Users should test and provide feedback based on prototypes. Software engineers can then make changes to the product or start from scratch, depending on the feedback you receive.
Design thinking might not be the solution to every complex software engineering problem, but it certainly does help if you’re looking to satisfy your customers better.
Applying design thinking to the development process can take your software from good to great.
In today’s app economy, where competition is fierce, user experience is often the difference between an app that fades quickly and one that earns loyal daily use.
How To Create a Viral Mobile App
There are many ways to measure the success and impact of a mobile app, including the number of downloads, revenue, and reviews or feedback.
All feedback measures help developers see the impact of their work, but the most accurate measure of an app’s success in today’s market is its ability to go viral.
What Is a Viral App?
A viral app is a mobile application that gains popularity through frequent internet sharing, eventually becoming a modern trend.
The attention garnered from this type of popularity is often more effective than paid promotion.
An app’s virality stems from both technical and marketing expertise. The two are dependent on each other.
For instance, even if you create a great app, without the proper marketing, no one would know it existed.
Technical features affirm the value of your app, but an elaborate marketing strategy is what defines how the app will reach its target audience and thrive in the market.
Unfortunately, going viral is tough, and only a few apps become viral overnight. But there’s no harm in trying.
How to Develop a Mobile Viral App
First and foremost, your app should have something valuable for users to share. Naturally, the main principle of virality is sharing.
Having something worthy of sharing is key to getting users to spread the word about their experience with your apps, such as their achievement in a game like Candy Crush or a new review on TripAdvisor.
Once you have that covered, there are a couple of other tips to keep in mind.
Make It Easy
It should be easy for users to invite friends to join and share their experiences. By simplifying this process, you eliminate any undue stress that will put off users from sharing your app or its content.
Going through a 10-page registration form, for example, will turn away potential users.
Create Additional Value
The value of your app should increase as your users become more dedicated. Giving access to exclusive features is a great way to reward users who dedicate a lot of time to your app. Users will get the impression that your app is well worth their time.
Market Your Mobile Viral App
People share things that they can connect with emotionally. It can be something valuable, funny, or unusual. Emotions are used in virtually every industry to drive market growth.
There are plenty of tactics that can improve the chances of your app going viral. These are four tactics that may help to stimulate your app’s success in the market.
Create Limited Access
Some form of limited access or a waiting list can create a sense of suspense and curiosity.
Those who receive access feel special and validated, while those who do not experience FOMO, or fear of missing out.
You can play with the emotions and expectations of your users to create interest within your target demographic.
Incentivize Users
Your app should reward users for sharing and inviting others to the app via a referral system. You should also create incentives to encourage users to use the app more often.
Incentives don’t have to be monetary, but the reward should meet the effort. ropBox offers free space as an incentive for new users. Some other apps give limited access to their premium option.
Depending on the nature of your application, you can choose a reward that is attractive to your users based on the specifications of your particular application.
Encourage Social Sharing
Consider using a hashtag or tag phrase to prompt users to share content. Apart from helping your app go viral, social sharing can benefit your brand, your marketing practices, and your customers.
With social listening, you can tune in to mentions of your brand or application. In turn, you will gain in-depth insights into your product, which can help you adjust and update the app to tailor the users’ experience.
Engage Your Users
Notify users about new rewards, competitions, and promotions. Please give them a reason to keep returning to your app.
After a while, the same routine becomes boring, and all the excitement fades away. Therefore, it’s crucial to introduce new thrills or experiences through your app, whether these are new features or simple contests.
How To Monetize a Mobile App
Global consumer spending keeps rising.
Not to mention, on average, users spend three hours each day on apps. With all this play, the real question is – why aren’t you getting rich?
Well, if lining your pockets is your primary goal, Trio can offer some advice.
Ads
The most direct revenue stream for applications is mobile ads. These are either placed as banners on an active screen or pop-ups that appear when a specific action happens.
Imagine a gaming app that shows you a mandatory 15-second ad every time you lose. App owners can use a mobile ad network to sell ad space. You’ll learn more about these networks further down.
Ad Removal
Ironically, apps sometimes let users remove ads for a small fee. Ads can be very annoying, and removing them can significantly improve user experience.
Since this isn’t an expensive investment, many users will take the plunge, ultimately earning capital for your business.
In-App Purchases
Another way to generate revenue is through in-app purchases. Such purchases can take the user experience to the next level.
Paired with a freemium strategy, you can provide users with a basic version of the application for free.
Once they’ve grown to like the app, you can offer them the option to upgrade. Some ideas include extra lives for a mobile game or free delivery for a food ordering app.
Affiliate Programs
By joining an affiliate program, you can get paid every time you refer users to other businesses.
The payout depends on the payment model you choose and the action that users have to perform, like making a purchase, downloading an app, or passing the first few levels of a game.
Premium Subscription
As mentioned above, some businesses choose to offer the basic version of their application for free to attract more users.
Unlike in-app purchases, which allow users to buy separate items and continue using the rest of the application for free, a premium subscription requires a purchase of access to the app on a weekly, monthly, or yearly basis.
Ideally, the features that premium subscriptions extend should be fitting for the price.
Other Devices
Apps can make money outside of the context of a mobile device. Certain apps like Netflix and YouTube have found their way into other ecosystems such as Smart TVs and video game consoles.
Mobile apps that are accessible from multiple devices will, of course, generate more revenue than otherwise. Therefore, the usefulness of your app will be the ultimate judge of success.
How Much Money Can You Really Make?
The average app maker earns $20,000 a year before taxes. This doesn’t sound very exciting.
But remember that the success of your app has a direct correlation to your own investment, not only financially but regarding the initial research you put in, the feedback you derive, and the marketing you govern.
Thanks to monetization strategies like in-app purchases, Pokémon GO grossed $800 million in 2018. This was due to its virality and the fact that games, on average, do better than other types of apps.
More recently, subscription-based fitness apps like Strava and Calm, as well as short-video apps like TikTok, have crossed billions in annual revenue by combining viral adoption with effective monetization models.
You actually have the opportunity to make a significant amount of money with your mobile app. But it takes a great deal of work.
Think hybrid monetization. Most successful apps don’t rely on a single revenue stream but combine ads, subscriptions, and in-app purchases for a diversified model.
How To Monetize a Mobile App With Mobile Ad Networks
Now your application is up and running, and you’re ready to start making money. You’ve heard about mobile ad networks before, but you’re unsure where to begin.
The gist of it is simple. As you start attracting users to your app, placing ads within it will lead to a consistent revenue stream.
Ad marketplaces connect advertising agencies with developers or app owners. Advertisements themselves come in different forms – video ad units, mobile app display ads, and native mobile app ads.
In-app ads can also be a viable option for applications that have recently been released and are still working on setting up paid features or subscriptions. You can start generating revenue for your app while the work is still in progress.
Take a look at some of the advantages and disadvantages of mobile ad networks.
Advantages:
- Most importantly, making money. Mobile ads have proven to be a highly convertible method of mobile app monetization.
- Increase in-app purchases. Users who engage with advertisements are more likely to spend money on additional items within the app.
- Improve engagement. Ads that are tailored to match your app integrate seamlessly with the user experience, helping to boost user engagement and retention.
Disadvantages:
- It can worsen the user experience. Mobile ads can be annoying and interfere with app usage. In the worst-case scenario, users may look for an alternative application.
- How much you earn depends on the quality of your traffic. It’s not enough to target the people who use your app; you need to target them correctly.
The following will give you some insight into some mobile ad networks that are worth considering for your new app.
Chartboost
Chartboost is a specialized ad network for gaming apps, boasting direct access to 800 million gamers through cross-promotional ads.

With their playable ads, users can interact with a free sample of the game. Data suggests that this form of marketing increases conversion potential.
No gaming app should go without this. And as far as mobile gaming ads go, Chartboost is a strong option.
Google AdMob
Google dominates web advertising, so it’s only natural that it’d be on the list. Combining the best-in-class ad technologies into one platform, Google provides a solid solution that scales easily and integrates well.
Google is pretty easy to use. They allow you to present your app in several different ways.
Their platform has cross-platform capability along with several other features, including free analytics.
Media.net
Media.net offers highly competitive cost per mille (CPM) payouts and is a very popular choice for mobile traffic monetization.
It offers one of the largest pools of mobile advertisers in the market with a wide selection of contextual, native, and display ads that are easy to implement.
The network focuses on providing simple solutions to its clients, improving their ad performance, and increasing ROI through data analysis.
Keeping ads relevant is key to a better user experience and a significant conversion rate.
How To Monetize a Mobile App With a Freemium Strategy
To ensure your app’s success, your monetization strategy needs to have a balance between revenue generation and user experience, as one is worthless without the other.
Many monetization strategies, such as advertising, can be irksome for users, which may result in lower engagement and loss of interest.
For this reason, the freemium app monetization strategy remains one of the most popular and user-friendly ways to make money with an app.
What Is Freemium?
The term freemium is a portmanteau consisting of two parts: “free” and “premium”. This describes a mobile or web application that costs nothing to download and use, but often includes in-app purchases or a paid premium version with additional features.
The main advantage of the freemium revenue model is that it can be applied to most applications.
If your application is practical and provides value to the users, there shouldn’t be a lack of demand.
Freemium gives you a chance to nurture and educate your free users before they convert into paid ones.
This revenue model generates numerous positive outcomes for your branding and market ranking.
When users decide to try it, the value of your app goes up, which creates buzz. Users who are excited about your app’s features will share your app on social media. If you’re lucky, the result is a viral app.
Building a good application is not synonymous with the success of your mobile app. You need to understand how to position it in the market to get noticed.
Freemium Models
Through the freemium strategy, you can offer users a free, simple, and valuable version of your application.
As users interact with your app, they discover the benefits of premium features, which ultimately encourages them to upgrade to the paid version.
Depending on the product or service, you can decide on your own freemium restrictions. There are some standard options.
Based on Features
Users have access to the app’s basic features only. To gain additional access, they must either purchase the full version or subscribe to a membership.
For example, Relax Melodies Premium is equipped with additional sounds and guided meditations as compared to its free version.
Based on Time
The user gets access to the full version of the application for a limited amount of time to test out the premium features.
Once the free trial period expires, they can either pay to continue using the full version or choose to return to the basic version. Free trial periods are often between one and two weeks long.
Based on the Number of Uses
In this model, the user has access to all application features, but only for a limited number of times. After this limit is reached, they must pay for an upgrade to continue using the application.
For example, Medium allows users to read only three stories per month. After reading three articles, you’ll be prompted to subscribe monthly for access to all content.
Based on Customer Type
This is a rare model because it requires a certain level of user verification. Autodesk would be a good example, where students can use their services for free, while everyone else needs to get a paid license.
Sister App
For this model, you will need to create a separate, premium version of your app. This way, you will have two apps on the market – one completely free and one available only with payment.
Giving users a free or discounted version of the application helps them understand what your app can do for them, how useful it can be, and why they should upgrade.
Security & Compliance Considerations
Users are more privacy-conscious than ever, and app stores enforce strict policies to protect them. Neglecting security can result in app store rejection, reputational damage, or even legal penalties.
Data privacy regulations such as GDPR in Europe, CCPA in California, and LGPD in Brazil continue to shape how apps handle user information.
If your app collects personal data, you need to provide clear consent flows and give users a way to manage or delete their information. The simplest step you can take is to build a transparent, easy-to-find privacy policy directly inside your app and keep it up to date.
Authentication and authorization also play a key role.
Multi-factor authentication, secure login methods like Apple or Google sign-in, and even biometric options are now considered standard. If your app serves different user types, role-based access ensures people only see what’s meant for them.
From a technical standpoint, strong data protection is non-negotiable.
End-to-end encryption should be in place wherever sensitive data is transferred, and only the minimum amount of information should be stored locally on a device. Secure cloud services and regular updates to dependencies or third-party libraries will help you reduce vulnerabilities.
Finally, app store compliance cannot be ignored. Apple and Google both maintain strict guidelines and will reject apps that request suspicious permissions, use insecure payment methods, or fail to disclose data practices.
Testing against OWASP Mobile Security standards before submission is now a best practice for most development teams.
Post-Launch & Maintenance
Once your app is live on the App Store or Google Play, the real work of maintaining, improving, and scaling it begins.
The first weeks after release are critical. You’ll gather feedback from early users, identify bugs that slipped through testing, and discover how your app performs under real-world conditions.
Acting quickly on this feedback not only improves the product but also shows your users that you’re listening.
Regular updates are essential for long-term success. These can range from small fixes that improve performance or security to larger updates that introduce entirely new features.
An app that remains static quickly feels outdated; one that evolves earns a reputation for being reliable and innovative.
Marketing doesn’t stop after launch, either. In fact, this is when it matters most. App store optimization (ASO), social media campaigns, and referral incentives all help to keep your app visible in a crowded market. Pair this with strong customer support, and you’ll create a cycle of engagement that brings users back again and again.
Then, you need to think about scaling. If your app grows faster than expected, your infrastructure must be able to handle the load. Cloud services make it easier than ever to expand capacity on demand, but proactive monitoring and planning are key.
The apps that thrive are those whose developers treat release as the beginning of a conversation with users, not the end of a project.

Subscribe to learn more about Hiring
Conclusion
Congratulations! By now, you should have the basic building blocks to develop your first mobile app.
To review, you’ll want to start with some in-depth research and an MVP. Then, you might want to start looking at some software companies that can help you build a team to develop your app.
Developing your app won’t be easy. That’s why it’s essential to implement strategies like design thinking into your development process.
Making money is another frontier that you’ll have to cross eventually. Luckily, you have a comprehensive list of monetization methods that will get your app booming on the market.
If you need help with any of this, don’t be shy. Reach out to Trio to learn more about the first steps and how you can get started today!
FAQ
How much does it cost to develop a mobile app?
The cost to develop a mobile app varies depending on complexity, features, and the team you hire. A simple MVP might cost a couple thousand dollars, while more complex, feature-rich apps can climb into the six-figure range.
How long does it take to build a mobile app?
The time it takes to build a mobile app can be anything from a couple of weeks to upwards of six months. This includes planning, design, development, testing, and deployment. The bigger and more complicated the app, the longer it takes to develop.
What’s the best way to monetize an app?
There is no single best way to monetize an app. Popular options include ads, freemium tiers, in-app purchases, and subscriptions. You need to consider your app and target market in your decision-making process, and you may even want to combine several to diversify your income.