Many companies use generative AI (artificial intelligence) in this day and age. Businesses are using these systems in their business processes to give them a competitive edge. The question is, how can you use generative AI technology for business?
Let’s take a look at what these different generative AI solutions might look like and how they might be useful to you. We’ll also look at some real-world applications and use cases so you can get a better idea of the practical results you can expect, as well as any business challenges that you might encounter.
If you need help building your own generative AI systems, you’re in the right place. At Trio, we provide companies with access to some of the top developers in the world, from Africa to Latin America. We take the top 1% of applicants and match each one to your project based on their experience and your requirements, so you can rest easy knowing you’ve got an expert on board.
But, before you can decide if you want to leverage the benefits of generative AI, let’s give you a better understanding of the technology behind it.
What is Generative AI and Why It Matters for Business
Generative AI is generally any AI system that creates new content. This could be text generators, which you’re probably very familiar with already, but also tools that generate images, video, code, or other data. This is opposed to more conventional AI models that focus on analysis or prediction in specific business processes, but we’ll discuss these differences more below.
Usually, generative AI’s ability to create this content relies on patterns it has learned from observing very large datasets. The larger the dataset, the better the result will be.
Large language models (LLMs) and other neural networks are usually the basis of many of these tools. These models use machine learning to learn the relationships, structures, and nuances in the data provided to them. The result is an output that looks almost like it was created by a human, making it incredibly useful for businesses.
How Generative AI Differs from Traditional AI
Generative AI models and traditional AI models are very similar to one another, but the key difference lies in their function. Traditional AI generally focuses more on analytics, categorizing data, making predictions, and recognizing patterns in very large data sets. Generative AI applications rest on using this information to create new content.
Common places people make use of generative AI capabilities include creative tasks, personalized customer experience, and even smaller roles in knowledge-based work.
In these cases, generative models can be thought of more as a collaborative partner than a purely analytical tool. Many businesses encourage their employees to make use of the models to assist them with writing marketing content, generating synthetic data for research, or developing product designs.
Key Terms and Definitions Every Business Leader Should Know
In order to make sure that you are able to keep up with developments in the industry, and that you can implement generative AI effectively within your business:
- Large Language Models (LLMs): The machine learning models that are pre-trained on large sets of data to the point where they can produce an output similar to that of a normal person.
- Prompt Engineering: Creating and refining inputs provided to AI in order to produce a desired outcome.
- Fine-Tuning: When you take a model with a more general purpose and customize it so it better suits your industry or the unique use you have for it.
- AI Agents: AI systems that need very little human intervention; they can start, execute, and revise multi-step tasks all on their own.
- Responsible AI: The ethical considerations that make sure you are using AI in a way that ensures transparency, fairness, and security in the business landscape.
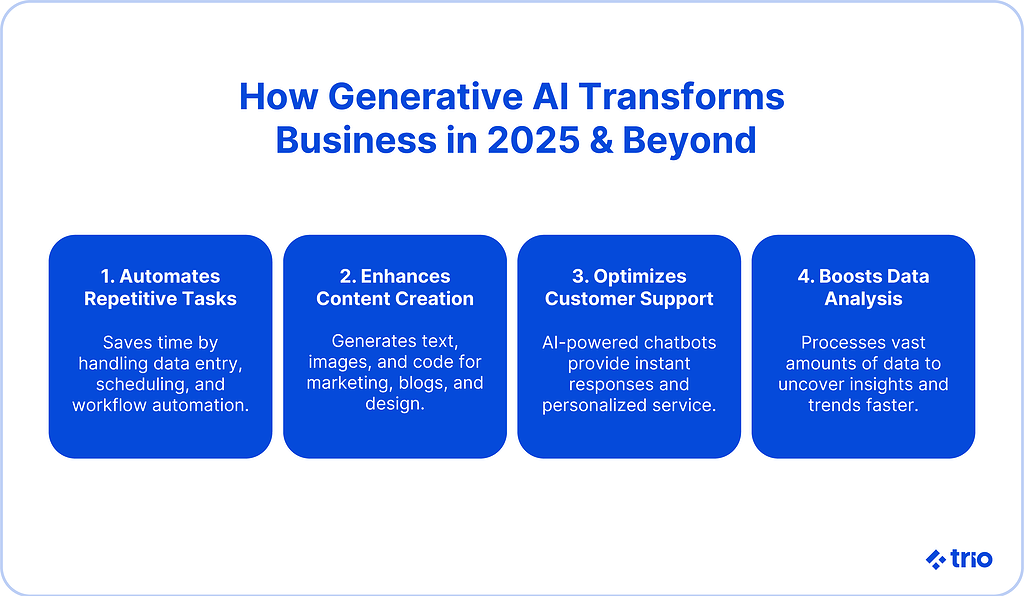
The Transformational Power of Generative AI in Business
We’ve already covered a couple of ways in which we commonly see AI being used in business operations. So, why is this revolutionary?
Why Generative AI Is a Game Changer for Enterprises
Previously, large amounts of manpower were needed in order to carry out creative or cognitive tasks. This meant that businesses were limited by the number of employees they had, the abilities of those employees, and the number of hours they could work effectively.
Now, generative AI has the potential to take care of a variety of these tasks in a way that allows incredible scaling.
If these models are deployed strategically, generative AI offers more business agility, reduces manual workload, and enables personalized, scalable content creation.
Since AI is taking care of all of these jobs, companies can make use of their human talent in other places where it might be more valuable and produce greater results in the business and society.
They also allow businesses to adapt quickly, enhancing resilience in even the most volatile markets and playing a big role in stabilizing the economy through digital transformation.
The Economic Potential of Generative AI: Market Value and Productivity Growth
Generative AI’s capabilities could have a $2.6 trillion economic impact just through enterprise use cases.
This money could come from everything from productivity improvement, cost savings related to changes in employment requirements, and even new revenue opportunities. Some companies may benefit from one of these cost savings while others might benefit from all three, and a couple more.
We expect to see some of the biggest impacts in industries where specific knowledge is required, and decision-making processes are quite labor-intensive.
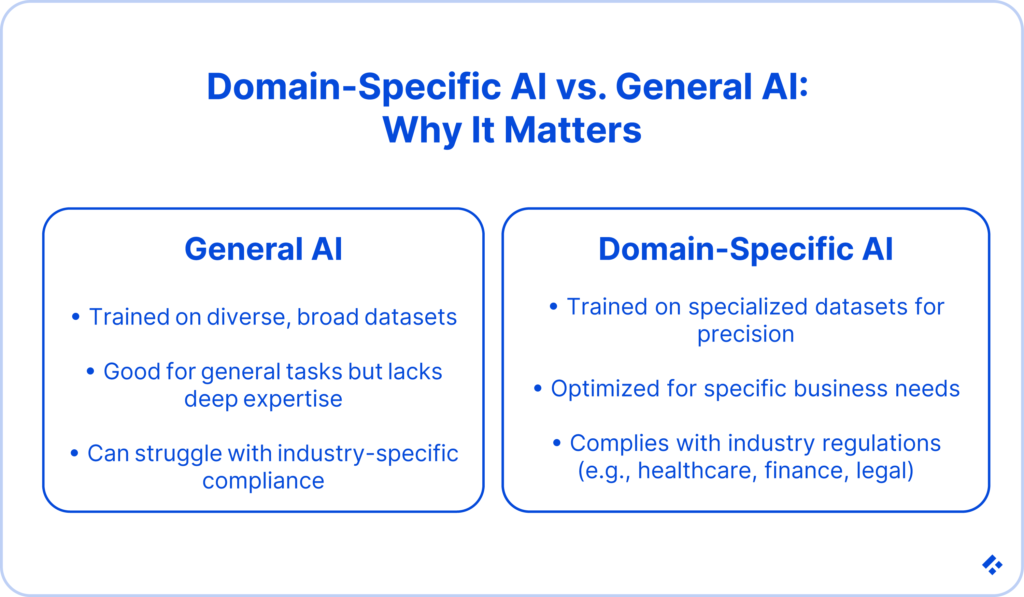
Domain-Specific AI Models: Why They Matter in Business Contexts
General-purpose generative AI’s potential is incredible. However, they are trained on large sets of data that often involve as much diversity as possible. This is great for preventing bias, but it lacks the specificity required if you want to use AI services in a specialized industry.
This is where domain-specific AI models take the cake! They are trained on proprietary datasets relevant to what you need them to do. The result is something that is incredibly accurate and relevant.
Domain-specific models are also able to focus on compliance with industry regulations. You may at first think this restricts them, but the reality is that it often frees you to use the AI in any of your business processes, instead of needing to restrict yourself to prevent legal issues.
For example, a healthcare provider might use a model that has been trained on large quantities of medical texts and case studies to make decisions based on a patient’s records without worrying about the information being used in ways the patient might not approve of.
Strategic Business Applications of Generative AI
There are a variety of industries that are already making use of generative AI to create value and practical solutions to their problems. Let’s look at the specific ways these tools are being used to transform business processes.
Customer Operations: Enhancing Experience and Reducing Costs
Customer service has previously been a very human-oriented field since it is so front-facing. Thanks to the capabilities of generative AI to appear so human-like, it can now be used to power chatbots and virtual agents capable of handling initial inquiries that may occur often, providing highly personalized support, and resolving a myriad of issues.
In the case of AI agents, many can complete all of these tasks without the slightest human intervention, and recognize when it might be time to pass the work off to an actual person.
We always like to think of the chatbots on home pages. Usually, you can ask a question and be given a tailored answer. If you don’t like the answer, or you have an issue that the chatbot can’t help you with, it might give you a ticket number or bring a real person into the chat. For most people, the chatbot usually gives them everything that they need.
The result is that you not only provide faster service to your customers, but also reduce operational costs.
Marketing and Sales: Personalization, Content Creation & Sales Productivity
Marketing and Sales will never be the same. Content can be generated automatically, although very few people recommend this, as no current generative AI model is perfect yet. It can also assist marketing personnel with research and iterations. This can include anything from blog articles and social media posts to personalized email campaigns.
Sales teams can also adopt generative AI technologies to generate usable insights. This allows them to identify promising leads, draft proposals, and tailor their outreach efforts.
All of this allows marketing and sales teams to make more informed decisions, which, in turn, leads to better results for the company as a whole.
Software Engineering: Accelerating Development and Reducing Tech Debt
Just like in marketing and sales, generative AI can assist developers by generating snippets of code. Most generative AI can also assist with debugging. In some cases, developers can integrate generative AI into the platform they are using to code, allowing for this debugging to become real-time, as well as allowing for features like automated documentation.
All of these features mean that AI can transform development cycles by helping developers code faster and more accurately. The result is reduced errors and minimal technical debt across IT departments.
With writing and testing code taking a lot less time, developers can focus on other, high-value tasks that address specific business challenges.
Product Research & Development: Faster Prototyping, Testing & Innovation
Product research and development is often incredibly time-consuming. But, leveraging generative AI means that you can generate a bunch of prototypes based on a single design in a matter of minutes.
AI can also simulate product performance and generate test scenarios. The result is that companies have a far higher chance of success when they actually start creating physical projects. In some industries, where a product fails, massive issues can arise, and this is especially vital.
Think of the automotive industry, where integral parts failing could cause people to get seriously injured, or worse. In these cases, running through a variety of simulations that cover as many scenarios as possible will allow businesses to guarantee the safety of their parts with more accuracy.
Risk Management & Compliance: Enhancing Decision-Making and Mitigating Threats
Risk management is a very data-driven field. The more data you can analyze, the more informed your decisions will be. AI makes it easy to look at large datasets and identify anomalies. In many cases, an anomaly can be identified in real-time. Think of finance, where fraudulent transactions need to be picked up as quickly as possible.
In many fields, you need to generate compliance reports and synthesize regulatory information. Generative AI enables instant updates to these reports, as well as the generation of figures and predictions, providing incredible business value.
Generative AI Use Cases by Industry
Although it hasn’t been around for very long, many industries are already using generative AI to transform their business processes. Here are just a examples we can learn from:
- Financial Services & Banking service: fraud detection, and personalized financial plans.
- Retail & Consumer Packaged Goods: enhanced product descriptions, personalized marketing content, and even inventory management.
- Pharmaceuticals & Healthcare: drug discovery, medical documentation, and personalized patient care.
- Manufacturing: creating digital twins, generating repair manuals, and streamlining quality control.
- Energy, Oil & Gas: demand forecasting and safety protocol generation.
- Transportation & Logistics: optimize delivery routes and improve supply chain visibility.
- Telecommunications: automate customer onboarding and manage virtual network operations.
- Aerospace & Defense: simulate defense scenarios and develop technical manuals.
- Insurance & Financial Institutions: streamline claims processing, risk assessment, and customer communication.
- Public Sector & Government: drafting policies, automating citizen services, and analyzing public health data.
- Education: providepersonalized learning content and automate grading.
- Tourism & Travel: itinerary planning, virtual tours, and content creation.
- Industrial Goods & Automotive: predictive maintenance, virtual prototyping, and process optimization.
Key Considerations and Risks for Adopting Generative AI
So, now that we’ve looked at other companies using AI to enhance their businesses, should you? Let’s look at some key considerations and risks generative AI poses.
Privacy, Fairness, Security, and Responsible AI Use
Ethics and security are two major considerations these days. People want to know that the people they are trusting with their information will keep it safe. They also want to know that the companies they work with aren’t prejudiced in any way.
Governments across the world are putting regulations in place to ensure that businesses remain compliant. Data privacy, fairness in AI-generated outputs, and protection against unauthorized access are all important aspects to consider when you are thinking of introducing generative AI in your business processes.
We always recommend that you be transparent about your AI usage, too. Doing so will help you maintain trust and accountability, especially in the client-facing sectors of your company.
Legal, Ethical, and Compliance Implications
We’ve already mentioned how governments are becoming stricter. The problem is that most of the issues surrounding the impact of generative AI are incredibly complex. These considerations span everything from intellectual property rights to data ownership and much more. This makes regulatory compliance quite complex.
It is best to get an expert on board as soon as possible. This can be a legal and compliance expert, but also a developer who is up to date on the latest training and implementation standards for AI and machine learning.
Companies like Trio are a great place to start. We hire only the best developers out there, and our focus on developer well-being means that our AI experts are able to focus on continued learning and staying up to date.
Environmental Impact of Generative AI
While it may not be obvious at first, the increased adoption of generative AI creates some serious environmental concerns. In order to handle the processing power and conduct effective data management, more data centers are being built. The facilities consume massive quantities of water and electricity.
While many are working on ways to mitigate the effect that the increased use of AI has on the environment, like experimenting with alternative cooling systems, there is still a lot of work to be done in order to make sure this new technology is sustainable.
This is a place we see a lot of potential at the moment, so if you are focused on sustainable technology, it may be worth your while to consider if there are any opportunities you could take advantage of.
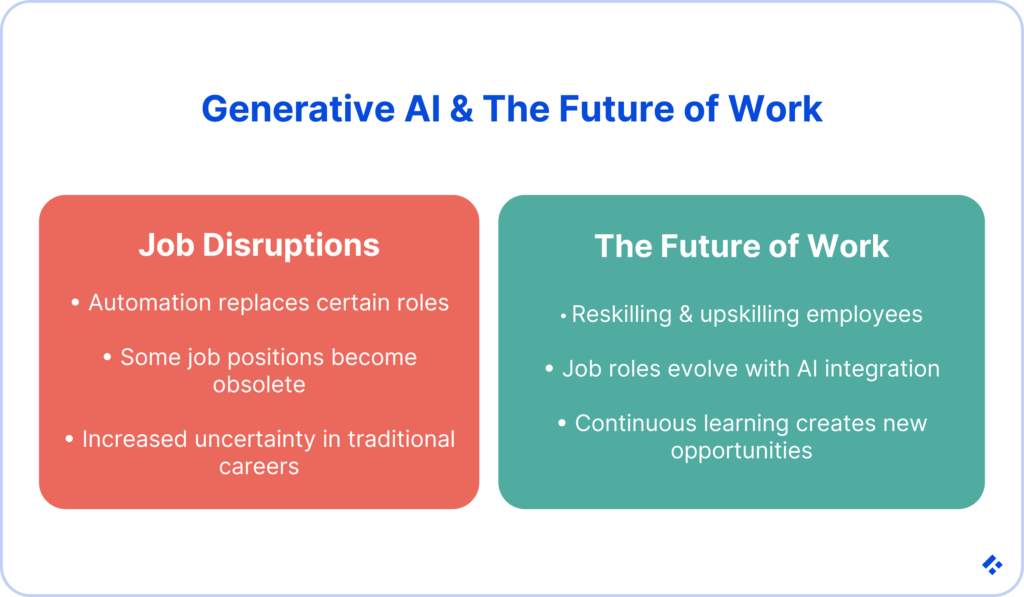
The Impact of Generative AI on Jobs and the Future of Work
The impact generative AI has on society is, in contrast, blaringly obvious. With AI transformation resulting in a lot of positions becoming unnecessary, a lot of people are losing their jobs. While this is no one’s fault in particular, businesses have a responsibility to their employees, and employees also need to step up.
The best response from both parties would be to focus on reskilling and upskilling. This could be done in the form of registered courses, or could even be done internally. Job roles can also be redefined in order to take on a few new responsibilities, while others are removed.
The idea is to focus on a culture of continuous learning, alongside a general understanding of generative AI’s impact, so that you are acting in preparation, rather than desperately scrambling as you react to changes that have already occurred.
How to Get Started with Generative AI in Your Business
If you think you should incorporate generative AI into your business processes, there are a few simple steps you can follow to set yourself up for success.
Developing an Enterprise AI Strategy
Before you start applying generative AI to every area you can think of – which can be a very expensive exercise – you should start by identifying the processes that might benefit the most. In order to ensure that your implementation has been effective, make sure that you select areas where you will be able to measure changes.
Doing this means you will be able to place a value on the AI impact and make an informed decision on whether you should try it in other areas, too.
It is important to make sure that you align your AI initiatives with any long-term business transformation goals that you might have right from the start. Create a scalable roadmap that will later guide you through the adoption process.
If you have no idea where to start with this, consider getting an expert onto your team, even if it is just temporarily. Someone with industry expertise will be able to create a detailed roadmap based on your company’s requirements, and will highlight potential risks and challenges you might encounter.
Best Practices for Generative AI Implementation
Many companies focus on the development process and making sure that they incorporate the latest advances in AI. But, if you forget to invest in talent development or staff training, you could have the best product on the market that no one can use effectively.
Similarly, you need to consider ethical principles from day one, or you might find yourself shutting the entire system down in the near future, or dealing with unhappy employees who think that they are going to lose their jobs. Being transparent about steps you are taking to mitigate negative effects – both internally and externally – will benefit you greatly.
If you are outsourcing development or integration to an external vendor, make sure that they are experienced in AI and working in the industry your business specializes in. This will allow you to maintain high standards in terms of both data quality and regulation compliance or governance.
The Future of Generative AI
Generative AI tools aren’t going anywhere. Although no one can predict the future, we can make certain inferences based on what we have already seen.
AI Agents and Autonomous Systems
Human intervention is still a must-have in a lot of cases, but AI agents and autonomous systems that can function almost entirely on their own are just behind the horizon.
We’ve already seen some major advances of these kinds of systems in some incredibly complex business processes. Finance and reporting, in particular, have seen some notable AI agent development.
Preparing for the Rise of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)
AGI is still a highly theoretical form of AI that can do anything humans can. It would be as smart as a human, with reasoning and – most importantly – adaptability.
There’s nothing close to AGI at the moment, but we should be prepared for a general movement in this direction. By understanding the value of AGI, we can predict how many companies will be training their large language models and how we should prepare to augment our skills and services to ensure that we remain relevant.
If you are thinking of using AI in your company and want to onboard some generative AI experts, you are in the right place. We have a host of experienced developers on hand who have not only worked with AI for several years, but are also familiar with a variety of industries.
If you want to start the process of matching a developer to your project, or you want to find out a little more about how AI could benefit you, reach out to us to set up a free consultation! As your trusted tech partner, we aim to promote business growth through technology.






