When you think about what makes fintech move so quickly (new payment apps, instant lending platforms, and digital-first banks), there’s one thing these players usually have in common: flexibility.
Under the surface, that agility often comes from a microservices architecture.
Instead of relying on one massive, tightly coupled codebase, fintech companies are breaking systems into smaller, independent services that can scale, update, and deploy without dragging the entire platform down.
In an industry where milliseconds matter and regulations never stop changing, microservices can make or break how efficiently a business adapts. That’s why you need to understand what they are and how they work.
If you need skilled fintech specialists with software development experience in similar projects, we can help you find the right people in a couple of days, not months, and connect you with them through cost-effective hiring models like staff augmentation.
But, before you consider hiring, let’s unpack how microservices architecture supports scalability in financial services, the challenges of implementation, and why so many fintech teams are embracing it as the foundation of their long-term digital strategy.
Understanding Microservices in Financial Services
Microservices architecture is a practical response to how software has evolved, and how fintech demands have outgrown traditional systems.
What Are Microservices?
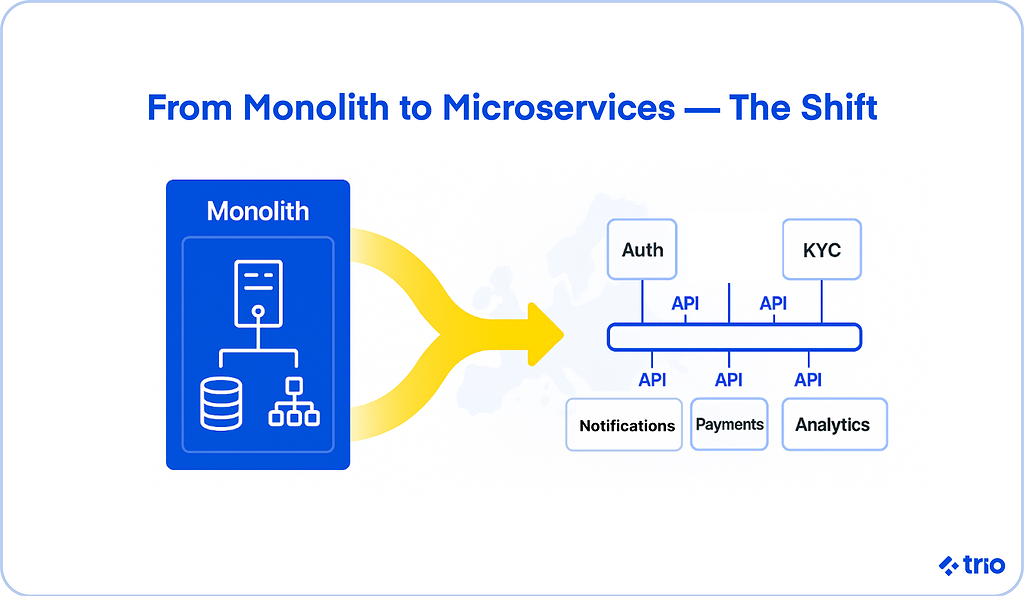
In simple terms, microservices split applications into smaller, self-contained components that handle specific business functions.
A lending platform might have separate services for credit scoring, document verification, and payment processing.
Each service operates independently, communicates through APIs, and can be deployed or scaled without impacting the rest of the system.
This structure contrasts sharply with monolithic architectures, where everything lives in a single codebase.
Monoliths can be easier to start with, but as fintech applications grow and regulations shift, they often become slow to update and difficult to scale.
That’s why getting cost-effective experts on your team early can make all the difference. Outsourcing from regions like LATAM, through fintech development firms like Trio, can make previously unaffordable talent accessible to companies of all sizes.
Core Principles of Microservices Architecture
Microservices rest on a few foundational principles that make them so adaptable for fintech systems:
- Decoupled Components and Independent Deployments: Each service functions on its own lifecycle, meaning updates can happen without interrupting other parts of the system, reducing the risk of something going wrong with changes.
- API-Based Communication and Lightweight Containers: APIs act as bridges between services, often containerized in tools like Docker or Kubernetes for predictable performance.
- Continuous Delivery and Fault Isolation: Teams can deploy updates quickly while isolating failures, ensuring that if one microservice fails, others keep running.
These ideas align closely with how financial institutions want to operate: agile, reliable, and auditable.
Monolithic vs. Microservices: A Quick Comparison
Think of a monolith like a single large bank branch handling everything, from customer onboarding to risk management to payments.
If one process slows down, the entire operation does.
Microservices, in contrast, resemble a network of specialized branches that each handle one function efficiently.
For growing companies in the financial services industry, this difference can be transformative.
We have seen how it enables faster updates, continuous innovation, and a more responsive approach to compliance and customer needs.
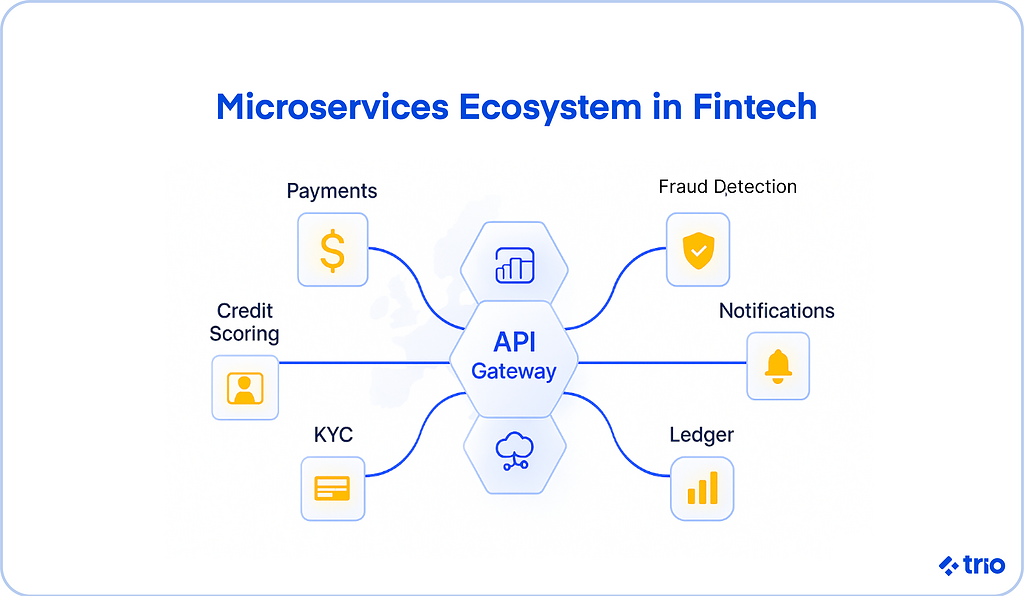
Benefits of Microservices in Fintech
The fintech landscape changes fast. Regulations shift, users expect real-time services, and transaction volumes can spike overnight.
Microservices architecture helps companies keep up without constantly rebuilding their systems.
Scalability and Load Management
Scalability is often the biggest reason fintech teams migrate to microservices.
Each service can scale horizontally, meaning you can add more instances of just the parts that need extra power, such as payment authorization during peak shopping seasons.
By distributing workloads across microservices, fintech applications reduce bottlenecks and maintain stability under stress.
Systems like Kubernetes automate this scaling, letting teams allocate resources dynamically instead of overprovisioning infrastructure.
Faster Time-to-Market for Financial Products
In fintech, being first to market can mean everything. You can build a customer base and build a reputation before your competitors enter the market.
Microservices make it easier for development teams to roll out new products or features independently. A new fraud detection module, for example, can go live without waiting for the next full platform release.
This modularity supports shorter development cycles, experimentation, and continuous delivery, all critical advantages in a competitive financial services environment.
Enhanced Security and Compliance Monitoring
Security in financial systems is never optional, and microservices can strengthen it, making it a big part of reducing risk.
Segmentation means a breach in one component doesn’t automatically compromise the entire system.
It also makes regulatory compliance easier by letting teams isolate sensitive workloads (like KYC verification or payment data) and apply stricter controls only where necessary.
Each service can log and audit transactions independently, which simplifies traceability during compliance reviews.
Improved Fault Tolerance and Resilience
When a monolithic app crashes, everything stops.
With microservices, failure in one service doesn’t necessarily ripple across the system. Circuit breakers and retry mechanisms contain errors before they spread, maintaining uptime even during partial outages.
This stability and reliability are major factors in customer trust.
A few minutes of downtime in a payments platform can cost millions and damage a reputation.
Easier Maintenance and Team Autonomy
Microservices also let small, focused teams take ownership of individual services.
Developers can work in parallel using different programming languages or frameworks suited to each service’s function.
Maintenance becomes easier because teams fix or update only what they own, improving overall efficiency and morale.
Scalability in Fintech Solutions
Payment systems, trading apps, and neobanks face unpredictable workloads that can grow exponentially. Creating a scalable payment infrastructure is essential for the longevity of your firm.
Our developers have helped countless companies retrospectively, but usually, changes to legacy systems are expensive, and damage has already been done to your reputation.
Why Scalability Matters in Financial Services
Transaction spikes are common in finance.
Think of Black Friday for digital payments or sudden interest-rate shifts affecting trading volumes.
Systems must handle these peaks in real time without collapsing or slowing down.
Scalability also enables global expansion. As fintech organizations move into new regions, they must support multiple currencies, languages, and regulatory frameworks, all while keeping performance consistent.
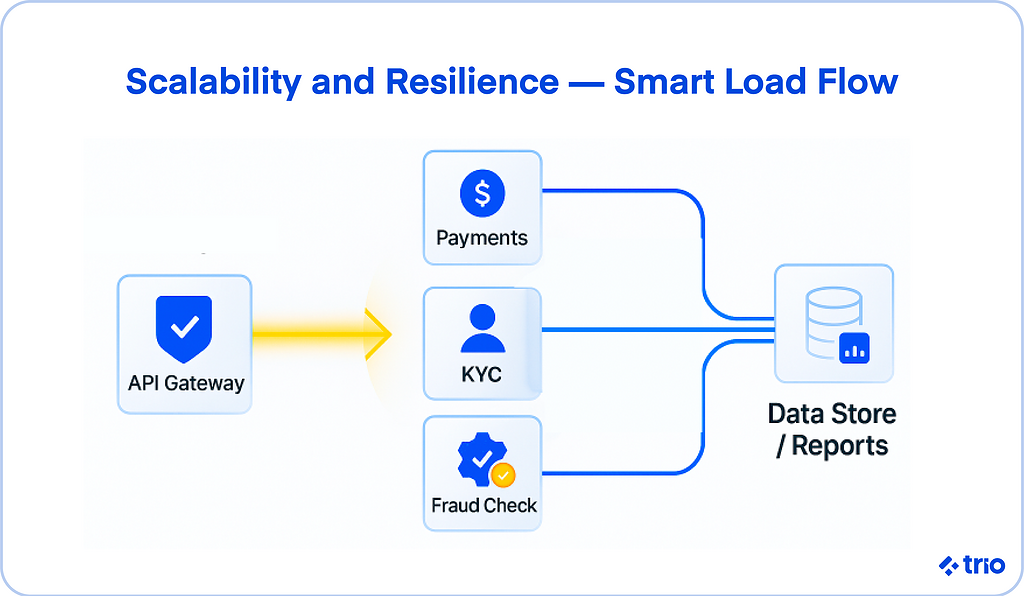
How Microservices Enable Elastic Scalability
Microservices architecture gives teams the tools to scale elastically, meaning resources adjust automatically to meet current demand. This happens through:
- Horizontal Scaling and Container Orchestration: Platforms like Kubernetes and Docker allow developers to scale services independently, keeping costs aligned with usage.
- API Gateways and Event-Driven Architectures: Gateways route traffic intelligently, while event-driven systems process transactions asynchronously for smoother performance.
- Load Balancing, Service Mesh, and Observability Tools: These help monitor system health and distribute workloads evenly to maintain reliability under pressure.
Together, these mechanisms create fintech systems that can handle rapid growth without compromising service quality or compliance.
Implementing Microservices Architecture in Fintech
Transitioning from monolithic systems to microservices requires careful planning. It’s less about rewriting everything at once and more about gradual adoption.
1. Assess Current Architecture and Pain Points
Start by identifying bottlenecks; maybe your payment processing is slowing down during high traffic, or compliance checks take too long.
Those problem areas often signal where microservices will add the most value.
2. Define Service Boundaries and APIs
Clearly define each service’s purpose and data flow.
APIs become the contracts between services, so precision here prevents confusion later.
3. Choose Technology Stack and Deployment Tools
Select technologies that fit your team’s expertise and compliance needs.
Docker and Kubernetes are industry staples, but fintech organizations might also rely on AWS ECS, Azure Kubernetes Service, or Google Cloud Run for deployment flexibility.
4. Establish CI/CD Pipelines and Monitoring
Automated pipelines keep updates frequent and safe.
Pair that with monitoring tools like Prometheus or Grafana for real-time observability and alerting.
5. Ensure Compliance Integration From Day One
Compliance isn’t something to bolt on later.
Incorporate regulatory requirements like GDPR or PCI DSS from the start by tagging and securing sensitive data appropriately.
Key Challenges in Deployment and Maintenance
While microservices bring scalability and agility, they also introduce complexity that fintech teams can’t ignore.
Data Consistency and Distributed Transactions
When multiple services handle related data, maintaining consistency is hard. Systems must synchronize updates without breaking atomicity, the guarantee that all parts of a transaction succeed or none do.
Fintech companies often use patterns like event sourcing or sagas to manage distributed transactions reliably.
Security, Authentication, and Authorization Across Services
With multiple services comes multiple access points.
Ensuring secure communication through token-based authentication and encrypted channels is essential.
Centralized identity management solutions can help maintain security without slowing performance.
Cross-Service Communication Latency
Microservices talk to each other frequently.
Each call adds latency, which can impact real-time transactions.
Optimizing APIs, caching, and using asynchronous messaging queues can reduce these delays significantly.
Regulatory and Audit Complexity
Decentralized systems have their use cases, but they can complicate audits.
Every service may generate its own logs, which need to be collected and correlated.
Fintech companies often deploy unified logging tools like the ELK stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana) to keep audit trails complete and compliant.
Best Practices for Fintech Microservices Development
A successful microservices environment is built through deliberate design and consistent maintenance.
Domain-Driven Design (DDD) for Financial Systems
DDD helps teams model microservices around real business domains like payments, onboarding, or account management.
It ensures services align with business functions and interfaces rather than arbitrary technical divisions.
Using API Gateways and Circuit Breakers for Fault Tolerance
API gateways manage traffic flow and protect backend services. Circuit breakers detect failing components and prevent system-wide cascades.
This is crucial for maintaining uptime in financial systems handling continuous transactions.
Implementing Event-Driven and Asynchronous Patterns
Event-driven systems use message brokers like Kafka or RabbitMQ to communicate between services without blocking.
This asynchronous approach enhances reliability and helps fintech applications handle large-scale, real-time workloads.
Monitoring, Logging, and Observability
Monitoring should go beyond uptime.
Fintech developers need deep visibility into transaction performance, error rates, and customer behavior.
Tools like Prometheus and Grafana help visualize metrics, while ELK stacks capture detailed logs for compliance and troubleshooting.
DevOps Synergy: Continuous Integration and Deployment
Collaboration between development and operations (DevOps) ensures consistent, automated delivery.
With CI/CD pipelines, fintech teams can push frequent updates safely, a must for maintaining competitiveness.
DevOps and Microservices in Financial Services
DevOps isn’t just about faster releases; it’s about creating systems that evolve safely.
The Role of DevOps in Modern Fintech Infrastructure
DevOps practices enable smoother deployment workflows, better version control, and faster rollback when needed.
It’s the backbone of reliable fintech environments where downtime is unacceptable.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) for Scalable Environments
Tools like Terraform or AWS CloudFormation let teams define infrastructure through code, making environments reproducible and auditable.
This reduces human error and accelerates scaling when demand spikes.
Testing Automation and Blue-Green Deployments
Automated testing ensures code changes don’t break critical payment paths.
Blue-green deployment strategies let fintech companies release updates to a small portion of users first, reducing disruption if something goes wrong.
Resilience Engineering: Chaos Testing and Failover Systems
Some fintechs intentionally simulate failures, a practice known as chaos testing, to ensure systems recover gracefully.
It’s a proactive way to validate resilience before real-world issues arise.
Security Integration: DevSecOps for Compliance-Ready Pipelines
Embedding security early in the development cycle helps meet compliance obligations without slowing delivery.
Static code analysis, dependency scanning, and policy-as-code tools all contribute to safer deployments.
Ensuring Compliance and Security in Microservices Architecture
Fintech systems handle sensitive data by definition, so every architectural choice must account for privacy and protection.
Handling Data Privacy (GDPR, PCI DSS, SOC 2)
Microservices should separate personally identifiable information (PII) and encrypt it both in transit and at rest.
Automated data classification tools help maintain compliance across distributed environments.
Secure APIs and Encryption
APIs are potential attack vectors.
Using rate limiting, OAuth 2.0, and TLS encryption keeps them safe while maintaining performance.
Access Controls, Auditing, and Role-Based Permissions
Each service should enforce strict access controls.
Role-based permissions and detailed audit logging make it easier to trace suspicious activities and prove compliance during audits.
Real-Time Fraud Detection and AML Integration
Microservices can enhance fraud detection by connecting transaction monitoring systems directly to AI-based analytics engines.
Suspicious transactions trigger alerts or freezes in real time, supporting AML and risk management initiatives.
Future Trends in Microservices for Financial Services
Microservices are still evolving, and fintech is pushing their boundaries.
The Rise of Serverless and Function-as-a-Service (FaaS)
Serverless computing takes microservices further by letting developers deploy functions that scale automatically.
It’s cost-efficient for workloads that fluctuate, a natural fit for fintech companies processing unpredictable volumes.
Integration With AI/ML for Predictive Fintech Operations
Machine learning models embedded within microservices can detect anomalies, optimize lending decisions, or personalize user experiences dynamically.
AI-driven microservices could become the backbone of next-generation fintech innovation.
Composable Banking Platforms and Open API Ecosystems
Open banking and composable architectures are redefining how financial institutions collaborate.
Microservices make it easier to connect third-party APIs, create modular offerings, and stay flexible as new fintech ecosystems emerge.
Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Deployment Strategies
To avoid vendor lock-in and improve reliability, fintech teams increasingly distribute services across multiple clouds.
This approach supports resilience and compliance across jurisdictions.
Event-Streaming Architectures for Real-Time Analytics
Technologies like Apache Kafka and Pulsar power real-time data pipelines, letting fintech platforms analyze transactions and behavior instantly.
These event-streaming systems are becoming essential for fraud prevention and dynamic customer engagement.
Conclusion
Microservices architecture has reshaped how fintech organizations think about scalability, compliance, and innovation.
It breaks systems into manageable, secure, and flexible components, exactly what financial services need to handle complexity at speed.
With the right tools, culture, and partnerships, financial platforms can scale confidently while maintaining compliance, performance, and trust.
If you need a trusted tech partner who can help you hire specialist fintech developers, you are in the right place.
Get in touch to find out more about hiring with Trio!
FAQs
What is microservices architecture in fintech?
Microservices architecture in fintech refers to building financial applications as a collection of small, independent services that communicate through APIs, allowing faster updates, better scalability, and improved fault isolation.
Why are microservices important for scalability in financial services?
Microservices are important for scalability in financial services because they let you scale individual components, such as transaction processing or fraud detection, without affecting the whole system.
How do microservices improve security in fintech applications?
Microservices improve security in fintech applications by isolating sensitive data, enforcing strict access controls, and enabling focused monitoring and encryption for each service.






