Companies choose to outsource software engineers for several reasons. Sometimes it’s to reduce costs. Other times, it’s to access skills and expertise that are not available through your in-house team.
IT outsourcing has evolved from a simple cost-cutting tactic into a strategic growth lever. Companies of every size, from fast-moving startups to global enterprises, now turn to outsourcing not only to save money but to gain access to specialized skills, scale quickly, and adopt critical technologies like cloud, AI, and advanced cybersecurity.
At its core, IT outsourcing means working with an external partner to deliver technology solutions. That might look like staff augmentation, where outside developers join your team directly. It could mean project outsourcing, where a partner takes ownership of delivering a specific solution. Or it may involve fully managed services, where an external provider oversees everything end-to-end.
A crucial part of software engineering outsourcing is trusting the team you’ve chosen. You will need to trust their expertise, their abilities, and their interest and involvement in the project.
Working with an outsourced software engineering team is associated with several risks that can negatively affect the delivery of your project. When you’re unfamiliar with the ins and outs of outsourcing, you won’t make the best decisions for your business.
But once you learn how to mitigate or avoid these risks and become well-acquainted with outsourcing in general, you can benefit from productive collaboration with a remote team. If this is your goal, keep reading.
We’ll walk you through the essentials of IT outsourcing in 2026: what it is, its advantages and disadvantages, the different models and regions, common risks, and future trends. Along the way, you’ll also see how to choose the right outsourcing strategy for your business.
What Is IT Outsourcing?
Outsourcing occurs when a business uses an outside supplier to obtain goods or resources, rather than relying on internal support.
Many branches of outsourcing, such as call centers, focus on reducing costs for large corporations. As a result, this is usually the impression people get of outsourcing in general. But small and medium-sized companies in the tech industry often outsource software engineers to gain an extra set of skills.
IT outsourcing is a flexible and cost-efficient way for your business to meet its technological needs without investing too much time and resources into hiring an in-house team.
IT outsourcing can also be a convenience for your internal employees. Their time might often be better spent on tasks unrelated to IT or software.
In broader terms, IT outsourcing covers far more than just hiring software engineers. It can include managed IT services, infrastructure support, cybersecurity, cloud migration, data management, and more. Companies may outsource entire functions, specific projects, or even build long-term partnerships with external providers.
It’s also important to distinguish between related concepts:
- Outsourcing: contracting with an external provider to deliver services.
- Offshoring: outsourcing to a distant country, often for cost advantages.
- Nearshoring: outsourcing to a nearby country with similar time zones and cultural alignment.
- Onshoring (domestic outsourcing): outsourcing within your own country.
- Managed services: a form of outsourcing where a provider takes responsibility for ongoing operations, not just projects.
What Are the Advantages of Outsourcing?
There are gains and losses on either side of outsourcing. Pay close attention to the advantages and disadvantages of IT outsourcing.
Many of the advantages of outsourcing highlight its convenience and practicality for small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs). The principal advantages of IT outsourcing are explained here.
Lower Costs
Cost reduction is likely the number one reason for outsourcing. Smaller companies, in particular, often lack the infrastructure, resources, and budget to develop their own IT solutions.
Taking care of their needs externally makes things simpler and cheaper. Offshore countries typically have lower costs of living as well. Thus, the overall price for outsourcing will be lower than that of outsourcing locally.
Risk Mitigation
IT outsourcing can get you guaranteed talent. Hiring talent yourself means you will be closer to the process. However, it can also pose a risk if you’re not well-versed in the technical skills you should be looking for in a candidate.
When it comes to actual development, too, an outsourcing agency like Trio is usually well-equipped with the tools and resources necessary to meet your needs. They have an abundance of experience meeting similar needs through their work.
Considering that an outsourcing agency’s primary objective is to meet your project requirements within your budget and timeline, you can maintain some certainty that your IT needs will be fulfilled successfully.
Access to Specialized Skills and Innovation
Outsourcing is about tapping into expertise that keeps your business ahead.
External partners bring in-demand skills in areas like cloud migration, cybersecurity, AI integration, and DevOps. With the right partner, companies can adopt new technologies and innovate faster than they could by relying solely on internal resources.
Scalability and Flexibility
Modern projects rarely follow a straight line, and outsourcing gives you the ability to adjust quickly.
Instead of committing to long-term hires, you can scale your team up or down depending on project needs. This flexibility helps meet deadlines and budgets without the overhead of permanent staffing, keeping your business agile in a fast-changing market.
What Are the Disadvantages of IT Outsourcing
The disadvantages of outsourcing generally involve a cognitive dissonance between the two parties working together, the internal managers and the external team. This disconnect can be the result of both physical and cultural circumstances.
Ineffective Communication
For a variety of reasons, IT outsourcing can lead to overall ineffective communication. Offshoring can lead to communication difficulties due to language barriers and cultural differences.
To work around this issue, many companies choose nearshore outsourcing as neighboring countries tend to share languages and cultural traditions.
You’ll learn more about nearshore outsourcing and different types of outsourcing down below in a separate section of this piece.
Idea Synchrony
Since you’re not sourcing your hires internally, there can be some lack of engagement between the IT team and business managers. They may not understand the full context of your vision or project.
That said, some outsourcing agencies make the extra effort to integrate with your internal team closely and with intention, so they can understand your project just as well as you do.
If this is the type of IT outsourcing you’re looking for, it’s essential to research the potential outsourcing agencies carefully before working with them.
Hidden Costs
Outsourcing can reduce expenses, but only if contracts are well-defined.
Vague agreements often lead to hidden costs, such as scope creep, unplanned change requests, or extra fees for project management and communication tools.
The safeguard here is clarity: detailed contracts and strong SLAs help prevent surprises and keep costs predictable.
Compliance and Data Security Risks
Sharing sensitive company or customer data with a third party always introduces risk.
Compliance frameworks like GDPR or HIPAA leave little margin for error, and weak data governance practices can expose your business to fines or reputational damage.
Working with partners who demonstrate strong cybersecurity and compliance processes is non-negotiable.
Vendor Lock-In
Relying too heavily on one provider can create long-term dependency.
If knowledge transfer and documentation aren’t prioritized, switching vendors later may be costly or disruptive.
Businesses can avoid lock-in by diversifying providers where possible, or by insisting on transparent, well-documented processes from the start.
When Is IT Outsourcing Recommended?
IT outsourcing is a good recommendation for businesses, particularly SMBs, who want to save costs without sacrificing quality.
While there is no doubt that tech-oriented companies want a high level of quality, sometimes they don’t have the means to supply it, whether that is due to a shortage of intel or resources.
IT outsourcing is an affordable solution that ensures skilled IT professionals or software engineers handle your project.
With IT outsourcing, you’ll find a trusted software development partner to address bottlenecks or give your next software development project a head start.
So, to summarize, IT outsourcing is recommended when:
- You need to scale quickly to meet deadlines, but don’t want to commit to permanent hires.
- Specialized expertise (e.g., cybersecurity, AI, DevOps, cloud migration) is needed but not available in-house.
- Budget pressures make it challenging to expand teams locally.
- Speed-to-market is a competitive advantage, and outsourcing accelerates delivery.
- Innovation is a priority, and you want external perspectives or niche expertise.
How To Outsource Software Engineers
There are multiple paths you can take for outsourcing IT talent. Understanding these paths in-depth will prove to be beneficial if you choose to outsource software engineers.
Let’s take a deeper look at a few of your options. You will have the chance to identify the pros and cons of each option and decide what feels like the best fit for your business.
Engagement Models (How Work Gets Done)
Freelancer Platformers
Freelancer platforms can be a practical solution if you’re on a tight budget and looking to get something done in a short time frame.
The gig economy is thriving at the moment, with websites like Upwork and Fiverr allowing businesses to hire freelance software engineers with ease.
The quality of talent on these websites varies greatly, as do the tools provided to you for managing your temporary hires.
Many websites offer integrated tools for operations such as payment processing and hours tracking. These features make freelancer platforms a viable solution for handling small technical undertakings.
On the other hand, these platforms have a reputation for delivering mixed results. And if you have a large project, you should consider other options.
Project Outsourcing
Sometimes it makes sense to hand over an entire project to an outside firm. This could be because your team lacks the necessary skills as a whole, or perhaps you don’t have a team of software engineers ready to go, and you want to build something promptly.
Project outsourcing is a relatively hands-off approach, which can be good or bad depending on your needs as a company.
Taking this less-involved approach to software development reduces the need for extensive internal training and realignment, effectively saving time for you to focus on other matters.
You can think of this approach as the plug-and-play method of getting a project done because it removes a lot of the overhead costs and administration that come with integrating a new staff member into your team.
Payments, relations with individual contractors, and training are the concerns of the hired firm, not you. This option is accessible and streamlines project management.
However, the lack of oversight and management with entire outsourced teams can be a drawback for those who prefer a high level of control over their projects. And you’ll still take on the responsibility of making sure the firm you hire delivers quality results.
Staff Augmentation
This is a trend in software development that has become more prevalent in recent years. Staff augmentation means adding one or more staff members to your team on a contractual basis.
The key difference between this method and outsourcing your entire project lies in the ability to integrate outsourced talent into your company and manage them directly.
One reason staff augmentation has become quite popular recently is that it is a flexible way to add and reduce staff as needed.
Some projects require a different amount of human resources at various points in time. Staff augmentation allows you to meet these demands in a way that is much more reasonable than hiring and firing in-house staff on a per-project basis.
Many companies prefer staff augmentation over outsourcing entire projects because it gives them more control over the process. It’s a familiar procedure for anybody who is already used to hiring in-house staff, except that outsourced staff is only temporary.
Some firms exist to provide staff augmentation services, offering developers for your project on a contractual basis. Imagine IT outsourcing as a library of software resources for you to use as needed.
A notable advantage of staff augmentation is the level of control you’ll have over your project and the people working on it.
The principal disadvantage of staff augmentation is the ongoing need to onboard contract staff, which could be better spent on development.
Of course, as staff augmentation becomes more widespread, the industry will implement streamlined ways of prioritizing the technological needs of businesses like yours.
Pricing models
When outsourcing, one of the first decisions is how to structure payment. The right pricing model depends on the type of project and how much flexibility you need.
Fixed Price
This model works best for projects with clearly defined requirements, timelines, and deliverables.
Because everything is scoped upfront, costs are predictable and easier to budget for. The trade-off is flexibility: if requirements change midstream, renegotiation is often needed.
Fixed-price contracts are a good fit for smaller projects or proof-of-concept where the scope won’t shift.
Time and Materials
Time and materials (T&M) is designed for projects that evolve as they progress. Instead of paying for a fixed scope, you pay for the actual hours worked and resources used.
This gives you flexibility to adjust requirements, experiment with features, and pivot if priorities shift.
The downside is less predictability in cost, so it’s important to track progress closely. T&M is common in Agile development environments where iteration is expected.
Dedicated Team
A dedicated team model gives you a stable, long-term extension of your in-house team. You’re essentially paying for a group of engineers who focus solely on your projects.
This setup is ideal for businesses with ongoing development needs, complex roadmaps, or products that require continuous improvement.
While more of a commitment, the benefit is alignment and long-term knowledge retention; your outsourced team becomes as familiar with your product as your internal staff.
Relationship Models
Outsourcing is also about the type of relationship you want to build with your provider.
Managed Services
With managed services, the outsourcing partner takes full responsibility for specific IT functions, whether that’s infrastructure monitoring, cybersecurity, or ongoing application management.
This model frees your internal team to focus on strategy, while the provider ensures day-to-day operations run smoothly.
It’s especially useful for companies that want reliable coverage in critical areas without hiring a large in-house operations staff.
Co-Sourcing
In a co-sourcing model, your internal team works side by side with the external partner.
Responsibilities are shared, collaboration is tight, and the arrangement feels less like outsourcing and more like team augmentation.
This approach is effective when you want to retain strategic control but still need outside expertise or capacity to move faster.
Build-Operate-Transfer (BOT)
The BOT model is designed for companies planning to bring outsourced capabilities in-house eventually. The partner sets up and runs a dedicated team, handling everything from hiring to operations, and after a set period, ownership is transferred to your organization.
This option requires upfront planning but can be a strong way to establish a presence in new regions or build capabilities you intend to internalize later.
The Different Types of IT Outsourcing
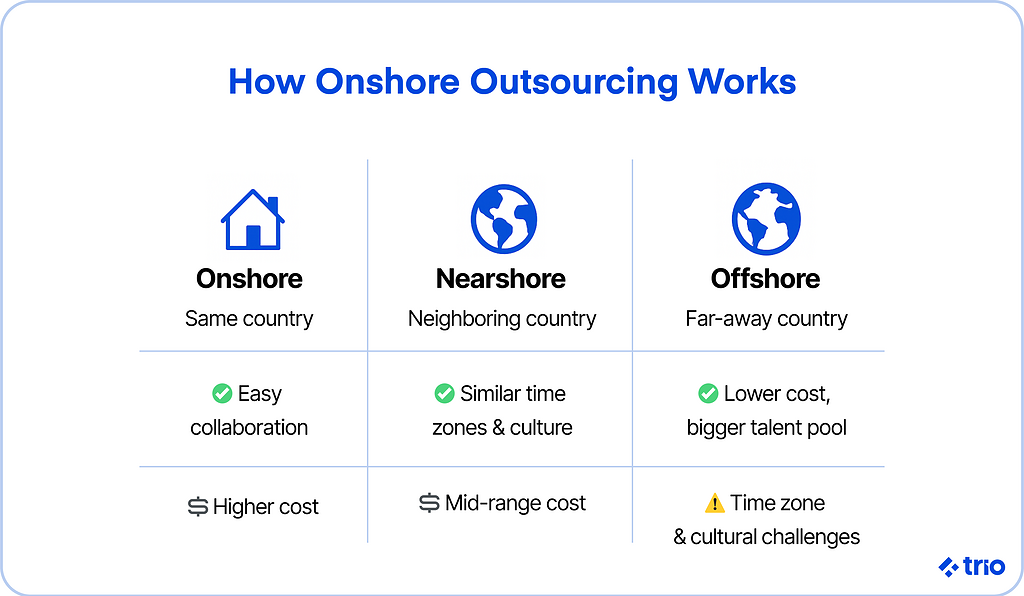
Typically, the outsourcing industry is categorized in terms of proximity and location. There are three main types of outsourcing you should be familiar with: offshore, nearshore, and onshore outsourcing.
OffShore
Offshore outsourcing is a general term for hiring external parties in a different country than your own to help with business operations.
Geographically, offshoring can also reference a more specific understanding that the country where you’re offshoring to is situated significantly far from your own.
For example, offshore development could delineate a similar distance profile as a United States company outsourcing to India or China.
The benefits of offshore outsourcing include major cost savings and access to large talent pools. The challenges often include time zone differences, cultural barriers, and communication hurdles.
Nearshore
Nearshore outsourcing can be considered a type of offshoring, as it involves outsourcing to a country other than your own.
However, the term implies that the country you’re outsourcing to is relatively close to your own and that there aren’t significant time zone differences.
In nearshore outsourcing, benefits include easier communication, cultural similarities, and overlapping working hours. Costs are usually lower than onshore, though higher than offshore.
Onshore
Onshore outsourcing refers to the practice of outsourcing to an external third party, but one that is located within your own country.
Also called domestic outsourcing, this can guarantee that there are little to no language barriers or cultural discrepancies.
The benefits of onshore outsourcing are convenience, cultural alignment, and easier collaboration. The drawback is typically higher costs compared to nearshore or offshore.
The Geography of IT Outsourcing
Geography influences the service price and talent of a given outsourcing provider. The customary market positions are shifting, revealing the new competitive countries in sight.
You can decide whether to outsource engineers onshore, nearshore, or offshore. These locational categories will also determine how exactly you go about managing your project.
Due to the high costs of domestic developers, companies seek technical assistance in foreign countries.
Asian countries like China and India are especially popular in the outsourcing world, and after so many years leading the market, the talent in this region is considered to be particularly reliable and high-grade.
At the same time, Eastern European countries such as Poland, Ukraine, Hungary, and Bulgaria have become highly competitive due to their strong technical education systems and English proficiency.
Latin American countries like Brazil, Argentina, and Costa Rica are also increasingly attractive, especially for U.S. companies looking for nearshore partners.
New markets are also emerging in Africa, particularly in countries like Kenya, Nigeria, and South Africa. These regions are gaining attention for offering competitive pricing, growing talent pools, and increasing government investment in technology sectors.
Nearshore locations are within two to four time zones of the central area of your business. This closeness in distance can alleviate communication and collaboration concerns. But you’ll still be saving money in the end.
Of course, you can always hire onshore developers in your own country, but this will likely lead to higher costs. The benefits would include low communication barriers, a predictable level of service, and possibly a location that facilitates in-person meetings.
When deciding where to find your IT outsourcing provider, it’s essential to know the exact requirements of your project, the allocated budget, and the time frame allotted for completion.
Don’t hesitate to look into less popular countries. You might find hidden talents at an attractive price.
7 Software Engineering Outsourcing Risks and How To Avoid Them
Understanding the risks associated with outsourcing software engineers can help you better identify your specific needs and determine the best fit for your business.
Much of the time, these risks align with what you would experience with an in-house team. Here are some common problems that arise when outsourcing developers.
1. Unrealistic Expectations
Unrealistic expectations happen all the time. You expect the project to be delivered yesterday, or the engineering team hopes to have more time for development.
Setting clear expectations for the project and communicating progress is the best way to avoid misunderstandings.
Conducting meetings in person or over video chat can really help everyone on the team communicate and deliver the project according to the client’s expectations.
2. Poor Communication
On more or less the same note, communication remains one of the most significant problems when outsourcing. Not only is it essential that the team has a means of communication, but they should also know how to communicate effectively.
Every project requires clear guidelines. This is even more vital for remote teams because you won’t be able to communicate your needs on-site in a face-to-face discussion.
3. Hidden Costs
There are many ways in which you can overpay for a project. Ironically, this can sometimes be due to striving for the lowest price possible.
Low-quality service, issues over source code ownership, poor documentation, and a lack of transparency during development are some examples of the problems you may face.
If you do not pay close attention to a company’s estimates and how you distribute your budget in the terms and conditions of your business relationship, be prepared for some unwelcome surprises.
4. Inadequate Technical Skills
The team can consist of skilled experts, but if the technical architecture and the framework of your project do not match, you won’t be able to make that collaboration work.
Proof of previous work skills and experiences in similar projects can ensure that the team you are hiring is a good match for your project. References can also help you identify if potential hires are a good fit for your project.
5. Poor Project Management
Project management is key to carrying out development projects. Good project management entails that business needs are addressed on schedule and within budget.
Providing the team with clear instructions and guidelines, offering regular feedback, and ensuring that tasks and resources are distributed correctly are only a few of the responsibilities of a project manager.
Poor leadership can fail the project, so it is crucial to ensure that the person in charge is capable of taking responsibility for a complex software engineering project.
6. Intellectual Property
Even if your idea is not unique or innovative, you should protect it. Using safe data processing methods and having engineers sign a non-disclosure agreement (NDA) or confidentiality agreement (CA) is the first step in protecting your intellectual property. But every situation requires a different approach and solution.
Finding a reliable software development partner will help you to eliminate most of the risks related to intellectual property matters. You should also avoid doing anything that can result in legal consequences.
Remember that the development project is a collaborative process, and as such, both parties need to be involved and responsible for the outcome.
7. Compliance and Security Risks
Relying too heavily on a single outsourcing provider can create long-term dependency. If knowledge isn’t properly documented, or if systems are built in proprietary ways, switching vendors later can become costly and disruptive.
The way to prevent this is by insisting on transparency from day one.
Shared ownership of code, thorough documentation, and clear exit strategies written into contracts ensure you’re never boxed in. With the right safeguards, outsourcing becomes a partnership built on flexibility.
Best Practices for Successful Outsourcing
Outsourcing delivers the most value when it’s guided by clear processes and shared expectations.
While cost savings and flexibility are big advantages, those benefits can fade quickly without the right approach. To make outsourcing truly effective, businesses should follow a set of best practices that reduce risk and strengthen collaboration.
Define Clear Goals and Expectations
Every successful outsourcing partnership starts with alignment. Before kicking off, set clear goals, success criteria, timelines, budgets, and deliverables. Ambiguity in the beginning almost always leads to misalignment later.
For example, if you’re outsourcing a web application, specify whether the partner is responsible for just the front end, the whole stack, or ongoing maintenance. The more precise you are about scope, the fewer surprises you’ll encounter mid-project.
Choose the Right Partner
Not all outsourcing providers are created equal. Evaluate potential partners based on technical skills, industry expertise, communication practices, and cultural fit. Case studies, client references, and small trial projects can help validate their capabilities.
It’s also important to look beyond the short term. A provider that looks good on paper but lacks stability or the ability to scale with you may not be a fit for a multi-year relationship.
Establish Strong Communication Channels
Communication is one of the biggest challenges in outsourcing, and one of the easiest to solve with the right practices. Agree upfront on tools (Slack, Teams, Jira, etc.), reporting formats, and meeting cadences. Regular check-ins build trust and keep teams aligned.
When working across time zones, overlapping hours are critical. Even a two- to three-hour window of real-time collaboration can make cross-border teamwork far smoother.
Use Contracts and SLAs Effectively
Contracts and service-level agreements (SLAs) protect both sides, but only if they’re detailed. Include performance standards around delivery times, quality metrics, security responsibilities, and escalation processes.
At the same time, the best SLAs aren’t overly rigid. They allow projects to evolve but still set boundaries for accountability. For instance, an SLA might define acceptable response times for critical bugs without prescribing how the provider achieves it.
Start Small with a Pilot Project
If you’re working with a new partner, begin with a smaller engagement before handing over mission-critical work. A pilot project validates whether the partner can deliver to your standards without putting too much at risk.
This approach is particularly valuable in sensitive industries like healthcare or finance, where trust and security are non-negotiable. A successful pilot builds confidence and sets the stage for long-term collaboration.
Integrate Outsourced Teams into Your Workflow
Outsourced staff deliver the best results when they’re treated as part of your team. Share your tools, processes, and culture so they can work seamlessly alongside internal employees.
Some companies even include outsourced developers in internal meetings or brainstorming sessions. These small gestures create a sense of ownership, leading to stronger performance and deeper engagement.
Plan for Governance and Long-Term Success
Finally, governance matters. Assign someone internally to own the outsourcing relationship, track performance, and ensure projects stay aligned with business goals. Think of outsourcing not as a one-off transaction, but as an ongoing partnership.
Regular reviews (quarterly is a good cadence) help both sides course-correct. Assess costs, performance, and alignment with your strategy. When providers see you’re committed to long-term success, they’re more likely to prioritize quality and innovation, not just meeting the bare minimum.
The Current State of IT Outsourcing
IT outsourcing as an industry is valued at about $588.38 billion in 2025, and expected to grow at 6.51% annually until 2030.
This growth is driven by several forces: the increasing demand for cloud migration, the rapid adoption of AI and automation technologies, and the ongoing shortage of skilled IT professionals in many local markets.
For small and medium-sized businesses, outsourcing has shifted from being optional to almost essential when competing with larger companies.
There is still a certain stigma associated with the idea of outsourcing. Even though most companies use outsourcing services, they prefer not to mention it. However, with the growing need for transformation and innovation, businesses require reliable partners to drive their growth.
The nature of IT outsourcing is changing. Where once the price was the deciding factor, value has come to the forefront. Companies are seeking proactive partnerships in return for detached third-party service providers.
Many organizations want their outsourcing providers to act less like vendors and more like collaborators who can proactively improve processes, enhance security, and contribute to product innovation.
Cybersecurity has also emerged as one of the most important drivers of outsourcing. With rising cyber threats and stricter compliance requirements, businesses increasingly rely on external providers that can deliver specialized security services, often beyond the capacity of an internal IT team.
Successful collaborations are based on quality supplier and client relationships. Customer-oriented outsourcing suppliers with tech-savvy specialists thrive the most in this climate. Their number one priority is providing value to their clients.
India and China are still leading the market for business outsourcing, but Eastern Europe and Latin America have gained significant traction as nearshore destinations. Many U.S. and European companies now see these regions as attractive alternatives thanks to overlapping time zones, cultural alignment, and competitive pricing.
The Future of IT Outsourcing
Just like any other industry, IT outsourcing will look different over time. You can be sure that some of its distinguishing traits will change or completely disappear in the next decade.
The following trends dictate the direction IT outsourcing is heading for the future. What can you expect to see in the years to come?
Partnerships
A transition from a third-party provider to a partner and collaborator is not a distinctively new development for the IT outsourcing industry. Still, it is certainly driving change in the industry.
Companies are seeking reliable and engaged IT partners who can offer new perspectives and share expertise where in-house teams are lacking.
An involvement that goes beyond simply following the instructions and offers informed opinions, active participation, and mutual ownership in projects provides value beyond just the service. This is the collaborative model taking over the IT outsourcing industry.
For this reason, features other than low costs are becoming the deciding factors in how businesses choose to outsource their IT needs.
Businesses expect outsourcing providers to contribute to product strategy, not just delivery. Providers that invest in building domain expertise and co-creating solutions are increasingly preferred over those offering only transactional services.
Team Modelling
A dedicated team model is relatively new in the outsourcing industry. However, in this outsourcing model, the outsourcing service provider and the client agree on the workload and timeframe of the project. Then the provider solely focuses on one project.
This approach allows team members to deliver projects in a shorter time period and with fewer errors. These models eliminate the need for multitasking, allowing a team to work on one project at a time.
Trio, for instance, offers Engineering Team Allocation (ETA), supplying client needs in the form of software development talent.
Whether it’s one developer or a team of software engineers, Trio seamlessly integrates developers into your project without disrupting your regular business processes.
This project-based approach can provide businesses with numerous advantages, including flexibility, team scalability, and cost-efficiency.
Going forward, dedicated team models are evolving into remote-first squads, where outsourced developers operate almost indistinguishably from in-house teams. Advances in collaboration tools, agile methodologies, and cloud-based development environments make this level of integration easier than ever.
Technological Optimization
In the past, outsourcing wasn’t a synonym for innovation. On the contrary, it was a way to reduce costs by delegating repetitive, time-consuming business processes.
Now emerging technologies like artificial intelligence, intelligent automation, and machine learning can do that and so much more.
You might not live long enough to see machines express feelings and emotions. And yet, you’ve already witnessed them becoming a part of your daily life.
Take chatbots, for example. They replace booking agents, customer support, call centers, and other similar services. The industry for this type of technology is growing at an alarming rate. Though it may be a threat to some jobs, it also creates new jobs and possibilities in different fields.
To accommodate, businesses must re-evaluate their processes. A successful business will upgrade its operations to become more effective and efficient.
Outsourcing providers aren’t just experimenting with AI in their own delivery processes; they’re also helping clients adopt AI-driven solutions. This shifts outsourcing from a cost-saving exercise into a true channel for innovation.
On the development side, AI is being applied everywhere from predictive analytics that guide smarter decision-making to automated testing that shortens release cycles and reduces human error. These tools speed up delivery while freeing teams to focus on higher-value work like design and product strategy.
Cybersecurity is also being reshaped by AI. Many outsourcing partners now offer advanced monitoring and threat detection, using machine learning to identify anomalies and flag potential risks before they escalate.
Outsourcing Smaller Projects
Small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) will play a bigger role in IT outsourcing. Outsourcing was once a privilege reserved for big companies. Now it’s the common tongue.
Niche providers aim to establish long-term relationships with clients by offering specific services tailored to the needs of small and medium-sized enterprises.
IT service providers undertake numerous smaller projects to enhance competitiveness and generate revenue.
Bigger contracts take much more time to be set up and are much harder to find. In turn, smaller projects provide flexibility and can often lead to larger jobs afterward.
Focusing on narrow niches also leads to multisourcing, where companies use several IT outsourcing providers for specific jobs or tasks. This helps businesses optimize costs and choose the best providers among niche experts for a long-term commitment.
For small companies, outsourcing is a competitive advantage, granting them access to more expensive and advanced technological solutions. There is a low barrier to implementation and maintenance. Ergo, SMBs can compete with larger and more established companies with little startup costs.
In other words, outsourcing is essential for SMBs to realize their growth potential sooner rather than later.
New Market Growth
As mentioned, countries in South America and Eastern Europe have begun to enter the international outsourcing arena. From their prowess, it is clear they have strong intentions to knock India and China off the pedestal.
Geographical proximity, high English fluency, and outstanding technical knowledge are valuable skills in the offshore development market. Therefore, developers from the above regions are appealing candidates for software development projects in international companies.
Economic conditions are something to consider as well. Global businesses seek out stable economies that are actively supporting technological development.
Africa has also emerged as a new outsourcing hub, particularly in Kenya, Nigeria, and South Africa. Governments are investing heavily in digital infrastructure, and a young, tech-savvy workforce is creating opportunities for affordable, high-quality outsourcing services. This region is expected to grow significantly over the next five years.
Does IT Outsourcing Sound Like Something That Could Work For Your Business?
Does software engineering outsourcing sound like something that could work for your business? If so, consider Trio as your partner for on-demand software development.
Trio onboards remote teams of software engineering experts onto your projects without disrupting routine business procedures. We stress the importance of customer satisfaction, delivering your projects efficiently and with high quality, no matter the complexity.
Contact us to get a personalized quote for your project!
FAQ
What are the risks of outsourcing IT work?
Common risks of outsourcing IT work include poor communication, hidden costs, inadequate technical skills, and security issues. But you can work around all of these with the right efforts.
How do I choose the right outsourcing provider?
To choose the right outsourcing provider, you need to start by defining your goals, budget, and expectations. Once you’ve done that, evaluate potential providers based on their technical expertise and their experience on similar past projects.
Can small businesses benefit from IT outsourcing?
Yes, small businesses can benefit from IT outsourcing as it allows them to access advanced technologies and compete with larger companies that have more resources.
What is the best way to outsource enterprise software engineering?
The best way to outsource enterprise software engineering is to define the scope clearly and choose a partner experienced with complex systems. Dedicated teams or staff augmentation work best at enterprise scale.
How do you outsource IT projects successfully?
Outsourcing IT projects successfully requires setting clear requirements and choosing a proven partner. Consistent communication and defined milestones keep delivery on track.
What are the pitfalls of outsourcing programmers?
The pitfalls of outsourcing programmers include unclear expectations and inconsistent code quality. You avoid them with strong documentation, code standards, and regular reviews.
Is outsourcing developers cost-effective?
Outsourcing developers is cost-effective because you pay only for the expertise you need. It cuts hiring costs while giving you access to specialized skills quickly.
What’s the difference between outsourcing IT and outsourcing developers?
The difference between outsourcing IT and outsourcing developers is the scope involved. IT outsourcing covers full operations, while developer outsourcing focuses on software engineering talent.
How do I protect my intellectual property when outsourcing software development?
You protect your IP by using NDAs, secure repositories, and clear ownership terms. Reputable partners also follow strict data and access controls.