Canada’s payment landscape is on the edge of a major shift. After years of preparation, Payments Canada is rolling out the Real-Time Rail (RTR), a new payment system designed to make moving money instant, data-rich, and available every hour of the day.
The system may not grab headlines like cryptocurrency or open banking, but its impact could be broader.
RTR will allow financial institutions, businesses, and payment service providers (PSPs) to send funds between accounts within seconds, safely and with immediate confirmation.
If all goes as planned, it will reshape how Canadians experience everyday payments, from bill pay to payroll to peer-to-peer transfers.
Let’s look at everything you need to know.
If you need skilled fintech developers who can help you take advantage of the new system and push ahead of your competitors, Trio can assist.
Understanding the Real-Time Rail (RTR)
The Real-Time Rail is part of Payments Canada’s long-term plan to modernize the Canadian payment system, alongside Lynx for high-value payments and the ACSS for batch clearing.
It introduces something the country has never had before: real-time settlement, operating continuously with finality guaranteed by the Bank of Canada.

What the Real-Time Rail Is
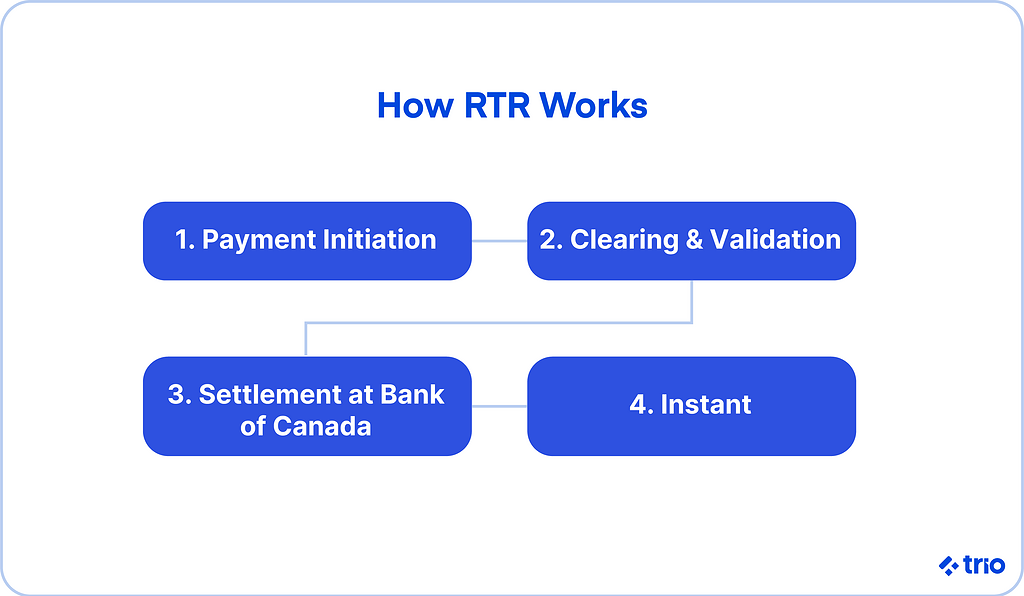
RTR acts as a new backbone for instant account-to-account payments.
Each transaction is cleared and settled almost immediately, meaning once a transfer is completed, it cannot be reversed.
The goal is to give Canadians and their businesses immediate, irrevocable access to their money, 24 hours a day, every day of the year.
Although the first live transactions are still ahead, testing is ongoing through 2026, and the technical build appears to be on track.
It’s a complex project involving governance from Payments Canada’s board of directors, oversight by the Bank of Canada, and coordination across banks, credit unions, and PSPs.
Related Reading: Open Banking and Account-to-Account Payments
Core Features and Capabilities
The RTR combines several important elements:
- Always-on processing with 24/7/365 availability, removing traditional banking cut-offs.
- Instant clearing and settlement, backed by a liquidity framework from the Bank of Canada.
- ISO 20022 message formats allow data-rich payments that support automation and analytics.
- Built-in tools for fraud management, such as confirmation-of-payee services that verify a recipient’s name and account before release.
It’s a big leap from the batch systems Canada still relies on today. Whether the transition is seamless will depend on how quickly institutions adapt.
Payments Canada’s Role in Modernizing the Payment System
Payments Canada operates the country’s national payment infrastructure under the Canadian Payments Act.
Its modernization agenda focuses on safety, accessibility, and flexibility, and the RTR is its most visible step toward those goals.
Mission and Modernization Goals
The modernization program aims to make payments faster and smarter while supporting economic growth and financial inclusion.
RTR brings this vision to life by providing a single, always-available system that serves banks, fintechs, and payment service providers alike.
You might note that Canada’s move comes later than many peers; systems like the UK’s Faster Payments or India’s UPI have been operational for years. But Payments Canada appears to be betting on quality over speed, building a system that is interoperable, safe, and secure, and future-proof for decades.
How Payments Canada Implements RTR
Developing a system of this scope requires coordination across policy, technology, and regulation. Payments Canada’s teams, supported by delivery partners, have been running comprehensive testing phases to ensure reliability before the platform goes live.
Participants will need to comply with both the Retail Payments Activities Act (RPAA) and Payments Canada’s own technical standards.
RTR’s use of the ISO 20022 messaging standard ties it directly to international systems, setting the stage for interoperability.
The Bank of Canada will provide liquidity management and risk control, a critical backstop in an environment where transactions settle instantly.
Collaboration Across the Ecosystem
RTR’s open design allows banks, credit unions, and PSPs to connect directly or through aggregators. Non-bank participants will likely play a key role in extending RTR’s reach to businesses and consumers.
This collaboration could unlock new competition, though it may also expose gaps in readiness among smaller players who are still upgrading legacy systems.
Innovation Through Real-Time Payments
The initiative promises not only faster transactions but also a foundation for broader innovation across financial services.
The RTR as a Global Benchmark
When Canada’s RTR becomes operational, it will join a growing network of real-time infrastructures. It sits alongside FedNow® in the U.S., SEPA Instant in Europe, and UPI in India, each shaped by its region’s banking culture.
Canada’s approach appears cautious but comprehensive.
It’s designed for interoperability from day one, ensuring that cross-border instant payments could eventually flow through shared standards rather than bespoke links.
The Value of Data-Rich Payments
The shift to data-rich payments may matter as much as speed. Each transaction on the RTR can carry structured information such as invoice numbers, payer references, or detailed remittance information.
That makes reconciliation easier and enhances fraud detection through improved context.
This could change back-office operations more than front-end experiences. Businesses might spend less time matching payments manually and more time using the data for forecasting and cash flow analysis.
Benefits for Payment Service Providers (PSPs)
For payment service providers, RTR opens doors to new business models.
Faster settlement and continuous liquidity can reduce funding costs, while real-time exchange of payment data supports added-value services such as instant payroll or small-business disbursement tools.
At the same time, not every PSP will find the transition easy. Meeting technical and operational requirements takes planning, and some may underestimate the cost of 24-hour uptime or new compliance layers.
At Trio, we’ve worked with PSPs and fintechs navigating similar upgrades in other markets. Our developers help integrate ISO 20022 messages, test APIs, and align with Payments Canada’s participation framework.
That hands-on engineering experience shortens timelines and reduces integration risk when every week counts.
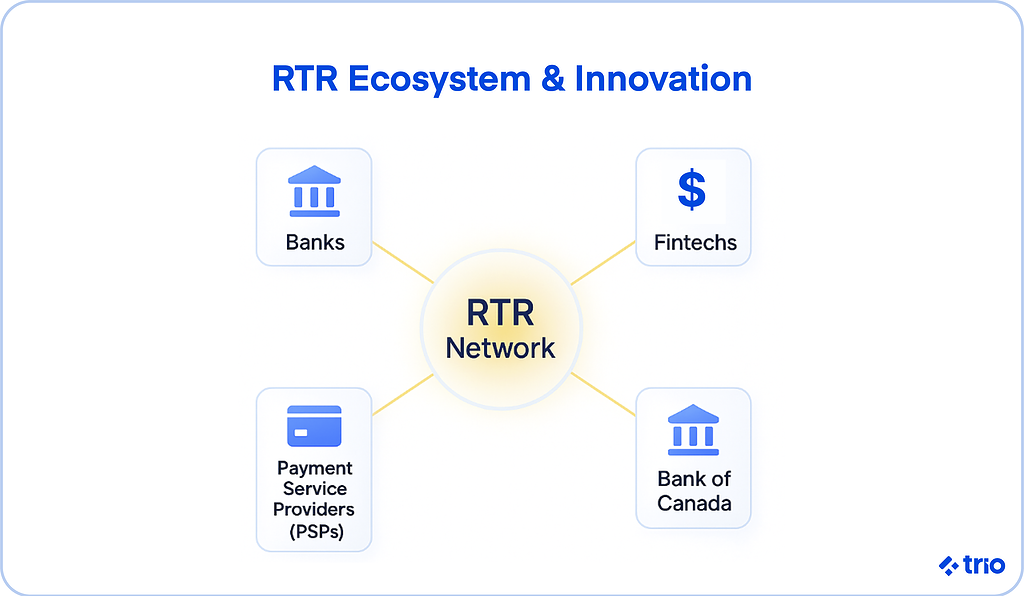
Participation and the RTR Ecosystem
RTR participation will shape Canada’s competitive landscape for years to come.
Who Can Participate
Direct access will be available to Payments Canada members who meet security and liquidity standards.
Others, including smaller PSPs and fintechs, can join indirectly through sponsored arrangements.
This layered model may seem restrictive, but it’s meant to balance innovation with stability.
Each participant must prove operational readiness, compliance with risk protocols, and the ability to manage liquidity in real time.
Ecosystem Impact and Opportunities
A functioning RTR could make the Canadian payment ecosystem more dynamic.
Faster transfers could help small merchants improve cash flow at month-end; consumers might see instant refunds from retailers; and government agencies could distribute benefits within seconds.
Still, ubiquity will take time. Even if RTR goes live on schedule, adoption will likely ramp up gradually as more participants complete certification.
Challenges for PSPs and Institutions
Integrating a new national rail isn’t all smooth sailing.
Institutions must retrofit legacy platforms, introduce centralized fraud controls, and ensure compliance with both Payments Canada’s and the Bank of Canada’s oversight rules. Smaller PSPs in particular may face steep technical integration costs.
That’s where Trio often steps in. We provide fintech-specific engineers who help payment providers implement new systems, design secure APIs, and run end-to-end RTR testing.
Clearing, Settlement, and Liquidity in Real Time
Behind every instant payment lies an intricate process of clearing and settlement that keeps funds moving safely and continuously across Canada’s financial system.
How Clearing and Settlement Work
As already mentioned, RTR operates on a continuous settlement model: each transaction clears and settles individually in seconds, backed by prefunded positions.
Liquidity management rests with the Bank of Canada, which monitors balances and mitigates systemic risk.
That design reduces settlement exposure but also demands precise liquidity planning from participants. A missed top-up could temporarily limit a PSP’s ability to send payments, a challenge that 9-to-5 treasury models weren’t built for.
Message Flows and Synchronization
RTR relies on standardized message types such as pacs.008 (customer credit transfer), pacs.002 (payment status), and camt.053 (statement).
These structures allow sending and receiving institutions to stay synchronized. In practice, that means every participant sees confirmation in near real time, vital for both compliance and customer trust.
Future Outlook
Payments Canada has signaled that cross-border connectivity is on its roadmap.
The eventual goal is an ecosystem where Canadian institutions can exchange payments with other real-time systems, potentially using shared APIs and common governance.
Such ambitions may take years to mature, yet the direction is clear. Real-time isn’t a feature anymore; it’s a baseline expectation in modern finance.
Conclusion
The Real-Time Rail is Canada’s bid to join the world’s leading payment infrastructures. It promises continuous access, data-rich payments, and stronger fraud controls, but its success will depend on how well participants adapt.
For PSPs and fintechs, the opportunity is significant, but only if their systems, teams, and compliance frameworks are equally ready.
We help those teams prepare.
By pairing vetted, fintech-ready developers with deep payments knowledge, Trio supports testing, integration, and long-term scalability within Payments Canada’s modernization framework.
If you are interested in adding these developers to your team, get in touch!
FAQs
What is Payments Canada’s Real-Time Rail (RTR)?
Payments Canada’s Real-Time Rail (RTR) is a new national payment system that will enable instant, data-rich payments between Canadian bank accounts 24/7.
When will the Real-Time Rail go live?
The Real-Time Rail is expected to complete its technical build in 2026, with final testing before official go-live once certification is complete.
How does the RTR differ from Interac e-Transfer?
The RTR differs from Interac e-Transfer by offering real-time settlement, ISO 20022 data standards, and full participation for financial institutions and PSPs.
Who can participate in RTR?
RTR participation is open to Payments Canada members and eligible payment service providers that meet security, liquidity, and technical requirements.





