As companies transition into the tech storm of the 21st century, the hassles of effective project management in the software development pipeline are escalating like never before.
Project management in software development is how you turn ideas into reliable software while staying both on time and on budget.
Whether you’re a rising startup looking to optimize total productivity and output of your software projects, or a well-established tech (or non-tech) corporation looking to scale your team’s software management efficiency, project management in software development is crucial to addressing all aspects of your business model.
Trio offers unparalleled software wisdom and access to South American developers. Meet our elite team of Colombian, Mexican, and Brazilian developers for outsourcing excellence.
Let’s go through how you would map the five project phases to the SDLC, choose the right methodology for your team, and track the KPIs that matter.
Are you ready to start your development project?
We have the developers you need to take your development project in the right direction.
Companies are proven to grow their business faster with Trio.
What Is Software Development Project Management?
Project management in software development is the process of planning, scheduling, executing, monitoring, and delivering software projects to ensure safety and consistency.
Oftentimes, when we envision the monster that is project management in software development, we fall down the rabbit hole of imagining a simple ‘one-size-fits-all’ project management model that mutually streamlines both the business and software-related (code) build and release of a company’s product.
However, software development projects can be better seen as complex undertakings, where leaders must analyze the cost-benefit and optimization problems between business value and the software development pipeline and processes.
In an ever-evolving landscape where business management and technology are closely intertwined, software development projects are complex tasks led by two or more people. Bounded by time, budget, and staffing resources, the goal is to produce novel or enhanced computer code with resource allocation and execution in mind.
More generally, software projects are defined by a comprehensive development pipeline, all the way from initial gathering to testing and maintenance, carried within a given timeline to achieve the intended final product.
Why Is Project Management Important in Software Development Projects?
Software project management is important because it ensures that there is a strategic method for accomplishing software-related objectives.
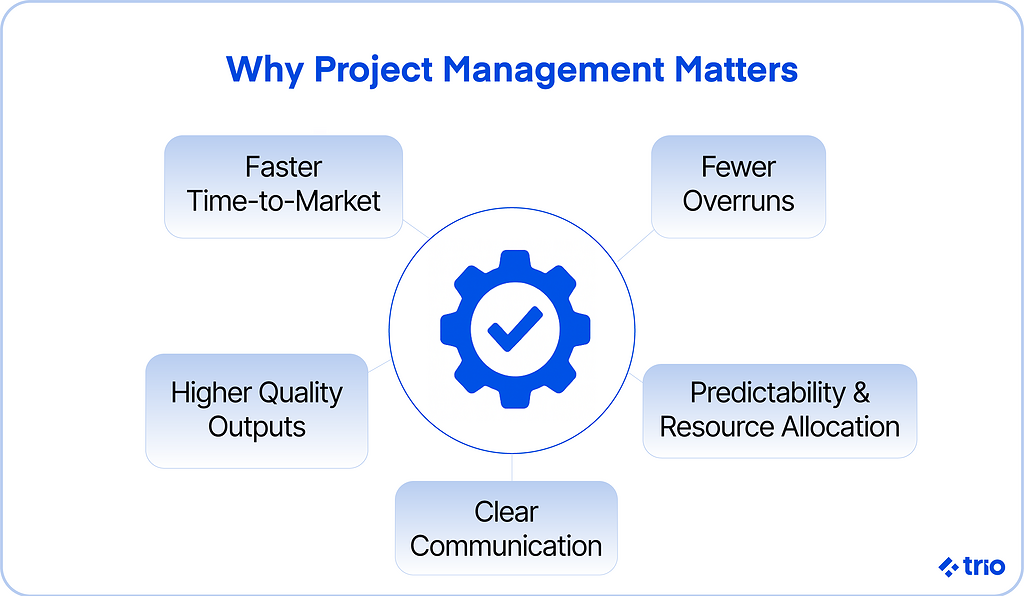
This adds significant business value to new/existing business processes and models. In practice, your business should see benefits such as:
- Faster time-to-market and reduced time-to-value
- Improved resource allocation and predictability of delivery
- Tighter budgeting and fewer costly overruns
- Clearer communication and stakeholder alignment
- Higher quality outputs and fewer escaped defects
- Better documentation and traceability for compliance or audits
In contrast to traditional project management models, software development is relatively unique, as software projects require a distinct lifecycle and phased development process that demands several rounds of user and internal testing, updating, and analysis of customer feedback.
As a result, project management in software development is a crucial part of delivering a quality product, and no development model would be complete without it.
What Does a Project Manager Do in Software Development?
Software project management is the ‘butter on the bread’, merging business management with the software development cycle. Project managers are responsible for efficiently executing all the nitty-gritty details of the software project from start to finish.
Most importantly, they are aware of all phases in the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) that the software project should undergo, streamlining the initial planning and long-term maintenance of the project at hand.
By closely monitoring the project management in the software development process, experimenting with various plans, allocating resources/budget, and solidifying communication amongst the team, software project managers ensure that final product goals are met under all constraints while still maximizing customer satisfaction.
All in all, project managers perform the following activities:
1. Project Estimation
Perhaps the most vital aspect of the initial project planning phase, project size estimation is crucial in determining the cost, duration, and projected efforts necessary for the project.
These estimations include:
- Time: Total projected time to complete the project and, if necessary, its subparts.
- Cost: Summary of total expenses to develop the software product.
- Effort: Estimated effort demanded to complete the project under any given conditions and constraints.
As a project manager, it is crucial that you accurately specify these time, cost, and effort estimations, as all future planning and executions are dependent on these projections.
2. Scheduling and Resource Allocation
In the context of project management in software development, project managers should schedule and allocate all required ‘manpower’ and resources for software project development after finalizing the estimations above.
3. Staffing
Establish and decide on a team structure and staffing plan. Gain feedback from the team on work burdens and their task progress to reallocate/reorganize the staff accordingly when capacity shifts.
4. Risk Management
As a software project manager, you must identify and analyze any unanticipated risks that might arise during the project development lifecycle through a risk log.
Devise your own risk reduction method to minimize/eliminate potential risks and unintended consequences during software development.
5. Miscellaneous Planning and Quality Assurance
Finally, catch your breath! During this stage, a project manager may establish several other plans, including quality assurance, configuration management, and other relevant project management processes.
Additional planning is conditioned on project monitoring and control, a cycle where the PM actively diagnoses potential risks and obstacles during development and uses planning to resolve those risks.
Most Important Skills a Project Manager Needs to Succeed
A project manager is not a monarch by any means. The role is more about orchestration and servant leadership than command-and-control. The idea isn’t just to put someone in charge and call it a day.
Project management is a careful undertaking and requires a unique skillset that not just any person can offer.
Here are the most important skills a project manager needs to succeed:
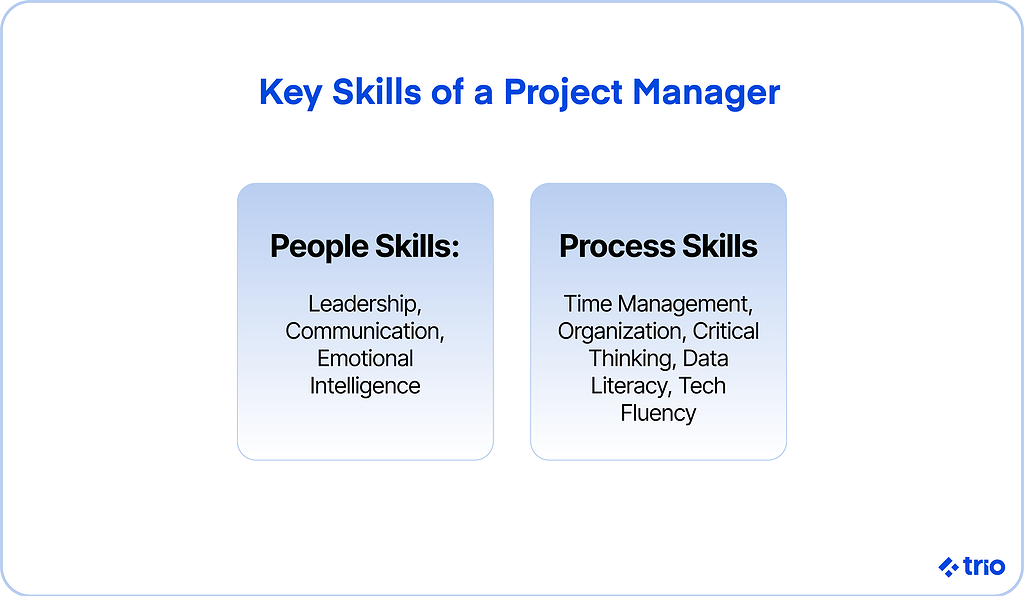
1. Leadership
Naturally, anyone managing a team should have leadership skills. But what does being a strong leader mean?
Strong leaders motivate their teams, coach them through task completion, and give them guidance on any issues that may arise.
Much of leadership is psychological. Technically, everyone on the team knows what they’re supposed to do.
But setting actionable goals, measuring team performance, and giving constructive feedback make a great impact on how the job gets done. A project manager is responsible for these duties.
2. Communication
Communication is an important skill in just about every industry. But it becomes increasingly important if you’re leading a team of software developers.
Project managers must have the technical expertise to communicate the details of the software project as well as the interpersonal skills to build and manage meaningful relationships with team members.
3. Time Management
It should go without saying that time management is an essential part of the project manager’s role.
Having a deadline isn’t always enough; often, what’s missing is someone behind the scenes to ensure everyone stays on task, making the machine run smoothly.
4. Organization
Organization is perhaps the most important skill for project managers. But it’s a broad term, and various factors play into one’s ability to organize, from communication skills to time management.
Simply put, a project manager should be able to see the big picture and break that down into the itsy bitsy details that make up a software development project.
They should also be able to break down those details into manageable tasks.
5. Critical Thinking / Problem-Solving
Often, project managers are the first responders when it comes to addressing bottlenecks and crises that pop up during development.
In order to successfully resolve these issues, they must be quick on their feet and think outside the box to come up with solutions.
6. Data Literacy
Modern project managers don’t just guide people; they also guide numbers. Being able to read KPIs, dashboards, and reports is critical to making sound decisions.
A good project manager doesn’t need to be a data scientist, but they should be comfortable interpreting performance metrics and using them to adjust timelines, resources, or priorities. This skill helps ensure that decisions are based on evidence, not just intuition.
7. Adaptability & Tech Fluency
Software development moves fast. New tools, AI-driven automation, and integration pipelines appear constantly. A project manager doesn’t have to code every day, but they should have enough technical fluency to understand what the team is working with.
Adaptability here means two things: keeping up with emerging tools, and adjusting when project requirements or technologies shift midstream. The best project managers know how to pivot without losing momentum.
8. Emotional Intelligence (EQ)
Perhaps the most underrated skill of all, emotional intelligence, is what keeps teams working smoothly under pressure.
High EQ allows project managers to recognize when morale is slipping, navigate conflicts between team members, and encourage people when deadlines get tough. More than any methodology or tool, this human element often determines whether a project succeeds or stalls.
Software Development Project Management Methodologies
Software development methodologies provide a structure for how you will go about building your software product.
These methodologies are also known as project management methodologies, as they provide guidance for organizing projects and achieving optimal performance through on-time releases.
There is no one-size-fits-all. Instead, think of it as a decision tree based on team size, complexity, and risk profile.
Below is an overview of some of the more popular software development project management methodologies.
1. Agile
Agile is by far the most popular software development methodology.
HubStaff found that 36% of software development teams are using Agile, with almost 40% of teams using a hybrid solution of methodologies.
Its core principles are iterative development, customer collaboration, and adaptability. Teams deliver working increments of software, gather feedback, and adjust quickly.
Based on an Agile manifesto written in 2001, developers collaborate with customers as they build software, iteratively implementing and testing software adjustments as they go.
Best for: projects with evolving requirements, startups, and fast-moving product teams.
2. Scrum
Scrum is an extension of Agile. It features a distinct system that helps developers approach the development process.
Much of what happens on a scrum team is managed via the concept of sprints, a short, time-boxed period of around 2-4 weeks allotted for completing a set amount of work.
The Scrum methodology similarly includes sprint retrospectives, sprint reviews, sprint planning, and daily scrums.
Best for: teams seeking structure and accountability in Agile practices.
3. Kanban
Kanban uses a visual board with tasks flowing across columns (To Do, In Progress, Done). It emphasizes work-in-progress limits and continuous delivery.
Best for: teams with high variability in tasks, support teams, or bug-fix streams.
4. Waterfall
The waterfall methodology emphasizes a linear progression of development.
It’s merely a step-by-step process of creating software from planning requirements to deployment. However, the integrity of this model is also its downfall. Professional developers rarely use this model because it does not adapt well to customer input, changing requirements, or unforeseen circumstances.
Best for: projects with stable requirements, regulatory environments, or government contracts.
5. Lean
The Lean methodology stresses the optimization of resources within a business. It stems from an operational thinking strategy that gave Toyota Motor Company its success.
In short, the fundamentals of the Lean methodology are to eliminate waste and create value for the customer.
Within software development, Lean thinking means foregoing extra features and preventing delays whenever possible.
Note that Lean and Agile are often confused. While some consider Lean to be a framework of Agile, comparing Lean vs. Agile reveals they are not as similar as some may think.
Best for: teams under tight budget/time pressure that need to maximize ROI.
6. Feature-Driven Development
Feature-Driven Development (FDD) is an Agile methodology for developing software. Like Agile, FDD is iterative, incremental, and customer-centric.
As the name suggests, FDD involves developing software based on its features and creating feature-specific teams.
Frequent status reports are also a mainstay in feature-driven development.
Best for: larger teams where modular development makes progress easier to track.
7 Best Project Management Tools for Software Development Projects
Project management works best with project management tools. Project management tools provide a platform for managing the software development process, whether that’s assigning tasks or setting deadlines.
The following project management tools should be plenty helpful for software development project management:
1. Trello
Trello is a web-based task-management tool that is based on Kanban project boards. Kanban itself is a framework that highlights the importance of visualizing workflows.
In the same vein, Trello uses boards, lists, and cards. Boards represent the overarching project while cards pertain to individual tasks. Drop-down lists indicate what stage your team is in completing a task.
In short, it’s best for lightweight task tracking, small teams, or visualizing simple workflows.
2. Wrike
Wrike is a project management tool with numerous high-tech features.
Like Trello, visualization plays an important role in how Wrike works. However, just as important as visualization to the platform are its capabilities. For instance, in Wrike, you can:
- Build workflows
- Set timelines for your projects
- Pin important to-dos onto dashboards
- Review and approve digital documentation
- Build reports and analyze results
Wrike has also recently added AI-powered risk monitoring to help you flag issues before deadlines become an issue.
We would recommend Wrike for mid-to-large teams that need flexibility across Agile and sequential methods.
3. Jira
Jira is one of the more popular project management tools. The tool specializes in issue tracking and Agile development.
Sprint tracking and Scrum workflows are beloved features of the platform, along with backlog management. Likewise, users take advantage of an open marketplace with integrations like GitHub, Salesforce, and Outlook.
4. Monday.com
Monday.com, typically stylized as ‘monday.com’, is a cloud-based platform that allows users to create tools and workflows to manage their projects.
In addition to project management, monday.com is a productive tool for various other efforts, such as marketing, sales, customer relationship management, task management, and human resources, with extensive automations and cross-team integrations.
Whatever your workflow may be, Monday.com can offer:
- Visual Kanban-style boards
- Multiple views (featuring boards, calendar, timelines, Gnatt charts, etc.)
- Custom dashboards (for tracking progress and insights)
- Integrations
- Automations
- Apps (for custom views, widgets, integrations, etc.)
5. Zoho Projects
Zoho Projects is a cloud-based project management software with an intuitive user interface coupled with many useful features.
Gnatt charts, task automations, timesheets, and project customization are some of the software’s biggest pros. You can also integrate Zoho with numerous third-party apps.
It’s a very affordable, all-in-one management, making it a good option for startups and SMEs on a tight budget.
6. Basecamp
Ironically enough, the notorious Ruby on Rails was created to build Basecamp. And it was undoubtedly successful.
Basecamp offers several features, including message boards, to-do lists, group chats, scheduling, automatic check-ins, documentation, and project activity dashboards.
In spite of all this, Basecamp isn’t designed for software development and lacks boards, estimations, and other helpful assets for Agile development.
7. Asana
Initially, Asana was an internal tool at Facebook. But released to the public, the tool quickly got its own bearings.
Asana features Kanban-style boards, Gnatt charts for project scheduling, and an advanced search engine for finding files and tasks. It’s great for hybrid teams that need structure without heavy engineering-specific features.
5 Stages of Project Management in Software Development
Whether you’re a junior or senior project manager, a common principle in the software development and management pipeline will always hold true: following and maintaining the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)
By adapting the SDLC process to your project timeline, you can streamline your project initiation, planning, monitoring, and closure, enabling the team to finish on time without compromising the project’s integrity.
Project management in software development essentially uses the general project management template with software-specific goals that streamline the process.
The 5 stages of project management in software development are outlined as follows:
1. Project Initiation
It may seem intimidating, but don’t worry, establishing a simple foundation of ideas and preliminary goals for your project will create a surefire template for the next four phases of your project management timeline.
Project initiation involves morphing an abstract idea into a meaningful goal with actionable future steps.
During project initiation, a PM should develop a business case and define the project on a broad level. Project managers can easily initiate this with a project charter.
A project charter is a document consisting of critical details, including project constraints, goals, appointment of the project manager, expected timeline, budget(s), staffing, etc.
Once a manager has illustrated a clear path forward with their charter, they should identify key project stakeholders (i.e., future members involved in the project). This can be easily accomplished by creating a stakeholder register.
In a project charter, two evaluation tools are used to decide whether a project is worth pursuing.
These tools can be tailored to optimize the process of project management in software development.
- Business Case Document: This document justifies the necessity of the project and includes an estimate of potential financial benefits.
- Feasibility Study: PMs use this to evaluate a project’s objectives, timeline, and costs to determine whether a project is worth executing. Feasibility studies allow you to assess a project based on its requirements and the availability of resources.
It’s important to note that although clear objectives of the project are established during the initiation phase, a project charter should not include complex technical details that are discussed in phase two (project planning)!
2. Project Planning
It is crucial that a project manager diligently lays out the project planning stage, as it is a decisive factor for the project’s roadmap.
Typically, this can be fulfilled with agile project management, effectively breaking down weeks of planning into mere days.
The PM should identify technical requirements and develop a detailed project schedule by creating a clear communication plan and establishing goals/deliverables.
Additionally, requirement analysis can be used during planning with inputs from the customer, sales department, market surveys, and domain experts in the industry.
For project management in software development, cross-collaboration is crucial, as it links the development team with the business management teams.
3. Project Execution
During project execution, all hands are on deck, and team members begin completing the actual work and subtasks of the project.
A project manager should look forward to establishing efficient workflows while diligently monitoring the collective progress of the team.
Additionally, a project manager must maintain effective collaboration between stakeholders and all team members involved.
Ultimately, this will ensure that everyone is on the same page and the project runs without any glaring issues.
4. Project Monitoring and Controlling
Although project monitoring is a process associated with each and every stage of the project management timeline, project managers should use this time to ensure that those project objectives and deliverables are explicitly fulfilled.
A project manager will ensure that no one deviates from the original course of the project by setting both Critical Success Factors (CSF) and Key Performance Indicators (KPI).
Finally, the manager will also quantitatively record and track the effort/cost during the process, ensuring that constraints such as budget and time are met with long-term sustainability in mind.
5. Project Closure
Finally, you’re here, phew! This final phase of the project management process typically follows after the final delivery of the product. Occasionally, external talent is hired specifically for the project on contract.
Additionally, a PM will be responsible for terminating these contracts and completing any necessary paperwork and documentation.
Oftentimes, teams will hold a reflection meeting upon project completion in order to contemplate their comprehensive successes and failures before, during, and after development.
This method of reflection provides a sense of continuous improvement for the team, enhancing the overall productivity and output of the team for the company.
Finally, a project manager should review the entirety of the project (from start to finish), complete a detailed report that covers all facets (e.g., five stages of project management in software development) of the project, and securely store it for future reference.

Elevate Your Team with Trio AI Talent
Empower Your Projects with Trio’s Elite Tech Teams
Conclusion
Whether you’re grappling with a large corporate team that develops cutting-edge software solutions or a small to mid-sized startup in the first round of creating their beta software, project management in software development is more essential than ever before.
By streamlining your software development process with a five-stage SDLC and project management timeline, your company is bound to finish and release final products in a timely and organized fashion.
However, to achieve this ‘holy grail’ of efficiency and organization, project managers must enthusiastically manage a team of developers and guarantee that deadlines are met!
For most companies, finding the right people to fulfill a project is like searching for a needle in a haystack, often resulting in missed deadlines.
However, you can outsource and hire remote developers to complete and build your team, guaranteeing that project deadlines and constraints are met. Learn more by reading our complete guide here!
FAQs
What is software project management?
Software project management is how you plan, organize, and deliver software projects through structured processes, tools, and team coordination. You use it to keep scope, quality, budget, and timelines aligned.
How do you manage a software development project?
You manage a software development project by defining scope, breaking work into tasks, setting timelines, assigning owners, and tracking progress. You revisit risks, adjust priorities, and deliver in iterative cycles.
Why is project management important in software development?
Project management is important in software development because it creates clarity around requirements, delivery dates, and responsibilities. It helps you produce reliable software on time and within budget.
What tools are best for software development project management?
Tools best for software development project management include platforms like Jira, Wrike, Asana, Monday.com, and Trello. You choose tools that support sprints, backlogs, integrations, and developer workflows.
What is an example of software development project management?
An example of software development project management is planning a two-week sprint, assigning tasks, tracking progress in Jira, and reviewing results in a sprint retro. You repeat this cycle until release.
What is the difference between SDLC and project management?
The SDLC explains how software is built, while project management explains how the work is organized, tracked, and delivered. You follow the SDLC stages while using project management to guide execution.






