Payment gateway integration is an absolutely essential feature for even the most basic MVP, and allows your company to monetize its products securely, even in later stages of its development lifecycle. It’s critical to get your payment processor to work correctly with the rest of your web and mobile apps.
Waiting until your product is already established is leaving money on the table, but at the same time, rushing the integration process or going with the wrong payment gateway provider could be incredibly detrimental, especially to your compliance strategy.
Let’s take a look at everything you need to know about integrating payment solutions, from choosing the right online payment gateway for you to ensuring that it enhances the user experience while complying with security and compliance requirements.
At Trio, we have developers who can assist with all of this.
Key Takeaways
- A payment gateway encrypts and routes payment data between your customer and all other parties involved, all in a matter of seconds.
- The right integration type depends on the amount of control your business needs over the checkout process, as well as your compliance requirements.
- PCI DSS compliance is incredibly difficult, sometimes impossible, to add on after the fact.
- Webhooks and proper error handling often determine whether a launch goes smoothly or causes real damage to customer trust.
- Costs include transaction fees, development time, compliance overhead, and the opportunity cost of a clunky checkout.
- Most smaller businesses benefit from integrating an existing gateway rather than building one from scratch.
What Is Payment Gateway Integration?
Payment gateway integration is the process of connecting payment gateway software, or a digital payment system, to your website or app.
For e-commerce platforms and financial service providers, this means your customers can make secure online payments using their credit and debit cards.
To provide users with the most convenience, a lot of businesses also integrate digital wallets like PayPal alongside basic gateways.
Although the basic versions of these integrated payment gateways have been around for quite some time, the more modern tools are focusing on improving the overall experience, whether this is through speed or regulatory compliance.
How Payment Gateways Work to Enable Digital Transactions
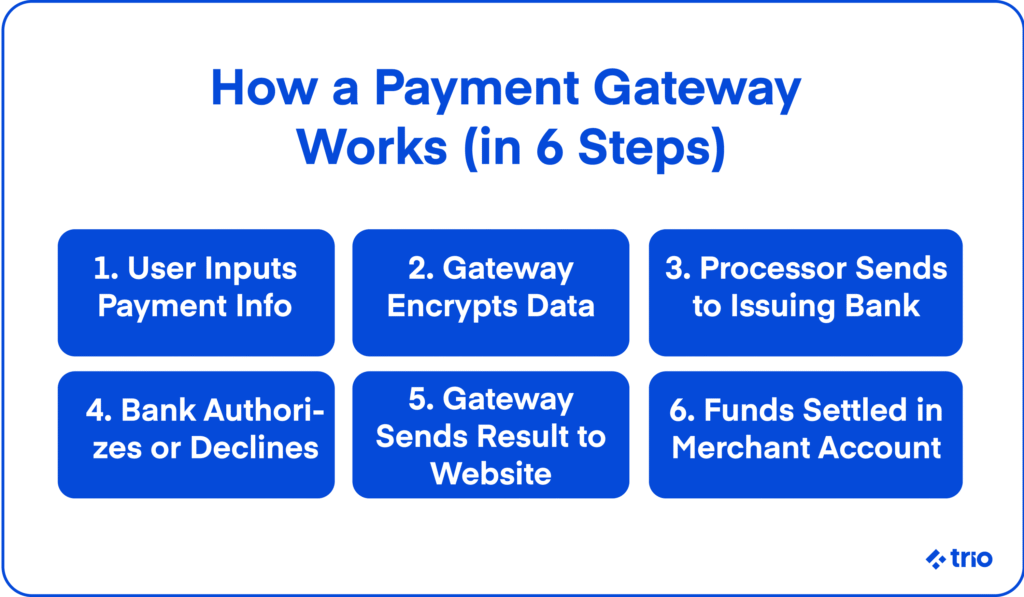
The pathway that payment gateways take to enable digital transactions is quite intuitive.
- The customer initiates a purchase and inputs payment details on your platform during the checkout process.
- The website sends the encrypted data to the payment gateway, provided that you have integrated it correctly.
- The gateway routes the request to a payment processor, which has either been bundled in with the gateway service or which you will need to choose separately.
- The processor seeks authorization from the customer’s issuing bank. They will usually have their own fraud detection methods and will ensure the user has enough funds available.
- Once approved or declined, the gateway communicates the result to the website.
- Funds are settled into the merchant account, often in batches later, including payment links for easier access.
As you can tell, it’s incredibly important that you have real-time processing abilities; otherwise, your customers will experience delays in their checkout experience and maybe even abandon the transaction.
Downtime will also directly lead to losses.
One underappreciated part of this flow is the role of webhooks.
Many payment events, like a delayed authorization, a chargeback, or a payout confirmation, do not get communicated back to your app in real time through the normal API response.
Instead, webhooks handle this by notifying your server asynchronously, so your system stays in sync with the gateway even when something happens minutes or hours after the initial transaction.
Payment Gateway vs Processor vs Merchant Account
It’s important to understand the different terminology used to refer to all of the different parts of the payment process.
- The payment gateway is like the digital point-of-sale terminal that supports local payment methods. It is what captures and encrypts payment data.
- The payment processor, on the other hand, actually handles the transfer of funds.
- The merchant account is your account, where the money ends up.
When choosing a payment gateway provider, you need to think about what exactly they offer. Some may be exclusively the gateway, while others may bundle all three and more.
Providers that bundle all three can simplify your operational setup considerably, since you work with a single support team and a unified dashboard. In some cases, pricing is simpler too.
The tradeoff is less flexibility in swapping out any individual component later.
Types of Payment Gateway Integration
Now that you fully understand the role that a payment gateway has in your ability to accept payments, let’s take a look at some of the best payment gateway integration options.
These include hosted gateways, integrated/API-based gateways, self-hosted gateways, direct post method, in-app gateway solutions, and custom-built solutions.
Hosted Payment Gateways
Hosted gateways redirect the user to a secure, third-party page that takes care of seamless payments and data security on its own.
They are probably one of the easiest to set up and completely remove any compliance burden, like PCI DSS, from your responsibility.
However, you don’t have any control over the checkout experience, making your choice of hosted payment gateways incredibly important.
It is also worth noting the distinction between all-in-one gateway providers and independent gateways.
Integrated Payment Gateways and API-Based Gateways
In these cases, your frontend and backend of your website or application are connected directly to the gateway. This is usually done using API or SDKs.
With integrated or API gateways, you have a lot more control over the UI, but it does mean that you need to deal with everything regarding security and compliance on your own.
Self-Hosted Gateways
Probably the most complicated web and mobile payment gateway integration method, but also the most flexible and customizable; all transaction logic and customer data are hosted on your own infrastructure.
Self-hosting is usually a suitable payment gateway option if you are a larger enterprise that needs custom workflows and data control, but also has the resources required to pull this gateway type off.
Direct Post Method
Direct post usually refers to when customer data is ‘posted’ to the gateway from the client’s browser.
While there is some decrease in the required security measures you need to implement in order to be compliant, you still need some careful security implementation.
Mobile and In-App Gateway Solutions
SDKs let you integrate all of your payment processing needs into your app directly.
Usually, this is the best option if you are offering some fintech service, like a digital wallet, peer-to-peer payments, or mobile banking.
Specialist developers have extensive experience in in-app gateway integration and many other ways to facilitate payments from customers in the fintech industry.
Local Bank Payment Integration
Local bank payment integration options are generally more regional, and providers offer integration for banks and mobile money platforms from a specific location.
If you are trying to target a specific country or region, this is a good option to avoid relying too much on international processors.
Custom-Built Payment Gateway Solutions
Building a custom gateway for your payment options is definitely the most labour-intensive and expensive of all of the options that we have covered, but if you have a unique business model or you work with very high transaction volumes, then it may be worth your trouble.
Just know that you are going to need to put a lot of time and money into security, compliance, and even network connectivity.
Essential Features for Modern Payment Gateway Integration
As we have already mentioned, a lot of modern payment gateways offer features beyond just basic payment capabilities. But, even if they are just payment gateways, not all-in-one solutions, there are certain features that have become industry standards to a degree.
Consider carefully when your chosen payment gateway has these features, and make sure to test that they have been integrated correctly.
- PCI-DSS Compliance and Secure Protocols
- Point-to-Point Encryption (P2PE)
- Fraud Detection and Prevention
- Tokenization and Data Encryption
- Subscription and Recurring Billing
- Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) Support
- Multi-Currency and International Support
- High Availability and Scalability
- Developer-Friendly APIs
- Robust Reporting and Analytics
- Omnichannel Payment Visibility
- Optimized Checkout UX
Unlike standard TLS encryption, point-to-point encryption scrambles card data from the very moment of capture, at the physical or digital input point, and keeps it encrypted all the way to the payment processor’s decryption environment.
If your business qualifies for a PCI-validated P2PE solution, this can reduce your compliance scope from hundreds of controls to just a few dozen.
That reduction in scope matters enormously when you are managing audits or preparing for enterprise deals, making this something we strongly recommend our clients look for in a payment gateway.
Omnichannel payment visibility is another feature we always keep an eye on.
As businesses increasingly operate across both in-store and online channels, a gateway that unifies transaction data from every touchpoint into a single dashboard can simplify reconciliation and reporting.
On top of that, it can be easier for you to identify trends that you might not have noticed if the data were more scattered.
Future Trends in Payment Gateway Integration
Like the rest of the digital market, payment gateways do not stand still.
The tools that felt advanced a few years ago are now basic user expectations. If you want an integration that still holds up in two or three years, there are a couple of trends you need to be aware of.
Digital Wallets and Alternative Payment Methods
Apple Pay and Google Pay, among others, reduce friction by skipping manual card entry and leaning on device-level security.
It might be worthwhile supporting these wallets, as you’ll probably improve conversion rates, especially on mobile, where typing card numbers feels like a chore rather than a feature.
Buy now, pay later options like Klarna and Afterpay have also become quite mainstream in checkout flows, particularly in retail and consumer goods.
Regional payment methods also deserve more attention than they often receive.
iDEAL dominates in the Netherlands, UPI processes billions of transactions in India, and ACH bank transfers remain the standard for B2B payments in the US.
Make sure you consider these regional trends, rather than just defaulting to card payments.
Tokenization and Advanced Encryption
These added security measures are quickly turning into baseline infrastructure.
Instead of storing raw card data, modern gateways swap sensitive details for tokens that hold no standalone value.
This approach shrinks your compliance exposure and limits the blast radius if something goes wrong, while still keeping recurring billing and one-click payments practical.
Stronger Customer Authentication
With frameworks like 3-D Secure and biometric verification, these features are gaining ground. Fingerprint and facial recognition checks may add a step, but they also cut down on fraud and chargebacks.
The trick lies in balancing security with flow, because too much friction at checkout quietly kills good transactions.
Smarter Fraud Prevention
Thanks to AI and ML developments, modern gateways have the ability to analyze behavior patterns, device fingerprints, and transaction history in real time.
While there is no way to guarantee this will eliminate fraud, there is a large chance it will improve accuracy.
This means you’ll reduce false positives, which means fewer legitimate customers get blocked at the worst possible moment.
UX-Focused Checkout Optimization
The best gateways now treat speed and simplicity as core features.
Fewer redirects, faster authorization, and even clearer error handling all play a role in enhancing the secure payment experience.
Over time, these small improvements often matter more to revenue than shaving a few basis points off transaction fees.
How to Choose the Right Payment Gateway for Your Business
When you are thinking about which payment gateway is right for your business, whether you are just thinking about the type of gateway or you are considering a specific option, like Stripe, you need to consider your business model and audience.
For example, if you are trying to run a SaaS business, you’ll encounter subscriptions or recurring billing, so you’ll need a gateway optimized for those transactions.
Also consider where your users are located, and how they prefer to make their payments. If you are a global business, you will need to support a bunch of different payment types and may have to make use of regional vendors.
The quality of documentation and developer support should factor into your decision, not just as a convenience, but because poor documentation leads to longer integration timelines and a higher chance of misconfiguration that could create security gaps or compliance issues down the line.
Choosing a reputable, actively maintained gateway also matters for long-term compliance.
APIs evolve, security standards update, and providers that invest in keeping their SDKs current save your team from discovering deprecated endpoints or unsupported authentication methods at the worst possible moment.
Step-by-Step Guide to Payment Gateway Integration Implementation
There are several steps you can follow to increase the chances of your online payment gateway integration being successful.
1. Technical Discovery and Scoping
First, you need to figure out what your requirements are. This can include the payment methods you need to support, expected transaction volumes, and even compliance.
You should take your tax obligations into account here to avoid costly mistakes going forward.
The more information you have before you start, the more accurate and efficient your technical decisions will be going forward.
2. API Setup and Authentication
Set up a merchant account with the payment gateway provider that you have decided to go with.
Your account will allow you to receive funds and will give you access to sandbox credentials and API keys, which will allow you to do things like test your integration without actually having to make a payment.
If you are creating a custom solution, you will need to create your own APIs here.
3. Backend and Frontend Integration
Once you have signed up successfully, you should be able to easily integrate your frontend and backend systems using SDKs or RESTful APIs.
If you are struggling, it is best to get an expert on your team.
You will need someone with the necessary technical skills required for API integration, as well as fintech expertise, to ensure these integrations are both secure and compliant.
4. ERP, CRM, and Checkout Synchronization
Once you’ve ensured that your gateway is connected to your payment screens, check your broader infrastructure.
Your ERP and CRM should be able to connect to your payment gateway for automated reconciliation, customer data updates, and even inventory tracking.
The latter is exceptionally relevant if you have a web or mobile commerce solution like an online store.
5. Webhook Configuration
As already mentioned, one of the most overlooked aspects of payment gateway integration is webhooks.
Gateways fire webhooks for events that fall outside the main request-response cycle: successful charges, failed payments, refunds, chargebacks, and payout confirmations all typically arrive this way.
Without a working webhook endpoint, your application may never learn that a transaction changed state after the initial API call, so it’s important that you set them up before you move to the testing phase.
To do this, you need to verify that your webhook handler validates the signature the gateway sends with each event and log incoming payloads (stripped of sensitive data) for debugging purposes.
We also recommend that you make sure your handlers behave idempotently, meaning that receiving the same event twice does not produce duplicate actions like double-shipping an order or double-crediting an account.
6. Sandbox and Live Testing
Most of the payment gateways out there offer some sort of sandbox mode for your various integration needs.
These sandbox tools are great for simulating things like successful transactions, failed transactions, refunds, errors, fraud detection, and anything else you can think of.
You can do thorough tests without needing to launch the payment gateway on your live app, ensuring that you aren’t caught by surprise when you move on to live testing.
One thing worth stressing is that sandbox behavior does not always match production exactly.
Certain payment methods or regional compliance checks may only surface in live mode.
While you should definitely treat the sandbox as your primary safety net, you can’t forget to keep close monitoring in place for the first 48 to 72 hours after going live.
7. Deployment and Go-Live Checklist
Quality assurance is critical, so much so that there are developers who specialize in it.
Once you are finished, you can move towards deployment.
Remember that your job isn’t just about the transition; instead, you should be carefully observing your transition to ensure you create a smooth changeover for your customers with the benefits of payment gateway integration.
Double-check anything related to security and data handling, like your TLS certificates, before you switch to live APIs, and make sure that everything still functions under real traffic.
Related Reading: API-First Banking and Automating Processes
Cost Considerations for Payment Gateway Integration
There are various ways that your payment gateway might incur some costs.
Setup and monthly fees are the most common costs that we see.
In some instances, startups and scaleups of a certain size might be able to take advantage of reduced setup fees or waive the fees entirely. If you are on a limited budget, this fee waiver will probably affect your choice of gateway from the start.
Per-transaction charges are also relatively common. These fees are often the most realistic if you don’t have a bunch of capital for higher initial costs, but they may add up long-term, especially if you are dealing with large transaction volumes.
You also need to consider how your users will primarily be paying, as transaction charges may vary by type.
Cross-border fees and currency conversion can be incredibly costly if you are consistently dealing with international transactions.
This is often a result of the different fees and processes required on the side of the gateway. If you are working within a region, you may be able to limit these fees.
However, it is almost impossible to avoid costs related to chargebacks and fraud handling. It is going to happen on occasion, even if you have the best security measures in place and the most comprehensive product in the world.
And then, of course, there are costs related to development, maintenance, security, and PCI compliance.
If you want to add more features later, which you may decide to do based on user demands or shifting markets, you will need to pay for all the additional development, integration, and testing as well.
This is all pretty standard, though.
One cost that we have noticed even large companies forget to factor into their decision-making process is opportunity cost.
While you may be able to save money using a cheaper plugin or fewer features, this can cause users to abandon their transactions, or even negatively affect their perception of your company and brand long-term.
Should You Build or Integrate a Payment Gateway?
Custom solutions make sense if you have the time and money to devote to them and need the added control that they provide, or you are struggling to deal with high transaction volumes.
It is also worthwhile if you have very niche requirements that no one else can provide.
In almost every other instance, it just isn’t worth it. The added internal expertise is often too costly to justify, even if you make use of nearshore or offshore development.
However, what many people may benefit from, and which our experienced developers can help you with, is a hybrid model.
In these cases, you would integrate multiple gateways for redundancy and risk management, or you could combine an existing gateway with custom development to get exactly what you need.
Compliance and Legal Requirements
PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) has been mentioned above already, but what exactly is it, and what does it mean for you?
In short, it is a framework that specifies how you should handle sensitive credit card data to ensure PCI compliance.
Instead of working in isolation, it is often complemented by the likes of EMV and 3-D Secure in an effort to reduce fraud.
You will have to deal with these regardless of where you operate, but there are also regional laws that you need to consider, like Europe’s GDPR and California’s CCPA. Both of these examples are related to data handling.
Consumer protection laws generally target data storage, consent, and reporting, so it is best to prepare as much as you can in advance, even if you are unsure of how you will scale regionally in the future.
Real-World Payment Gateway Integration Examples
There are many real-world payment gateway integration examples that you can look at when considering your own, including a few from some very notable names like Walmart, Lyft, and Due South.
Walmart + PayPal
Walmart partnered with PayPal on an enterprise level to allow its customers to check out on their online platform. Thanks to PayPal’s digital wallet, users don’t even need to enter their card details on Walmart’s platform.
The result is both an increase in conversion and overall user trust thanks to PayPal’s established fraud prevention systems.
Lyft + Stripe
Lyft partnered with Stripe in one of the biggest examples of gateway APIs. Stripe handles everything from user payments to driver payouts, while ensuring tax and banking compliance.
Stripe allows Lyft to manage everything related to these services in real-time, too!
Due South + Square
Due South benefited from Square’s all-in-one platform, allowing it to combine the tools that it was using in-store and online to unify the overall payment experience.
This also made it a lot easier for the company to manage its stock and finances as it could refer to a single dashboard.
All of this was made possible with relative ease, as Square is known for its quick setup.
Mistakes to Avoid in Payment Gateway Integration
People often fall into the same set of traps when integrating payment gateways for the first time. As you will notice, most of these mistakes are entirely avoidable if you get someone with extensive experience on your team.
- Choosing the wrong provider may lead to a generally poor experience for your users and make it difficult to scale later.
- Ignoring PCI compliance from an early stage makes it expensive to integrate later on.
- Failing to test everything that you should, even if it seems incredibly unlikely that things will go wrong, and not putting a system in place for documentation, can also make the overall user experience terrible and may massively impact your brand.
- Skipping webhook setup is another mistake that catches teams off guard post-launch. Without proper event handling, your system may report a successful payment while the back end never actually fulfilled the order, since the confirmation arrived asynchronously and had nowhere to go.
- Integrating outdated SDKs or failing to track API deprecation notices can introduce fragile code that breaks silently. Payment APIs do evolve, and a gateway that worked perfectly twelve months ago may behave differently today if your libraries have not kept pace.
Conclusion
Integrating payment gateways is largely unavoidable if you want your users to be able to make online payments of any kind. Whether you are using something like Stripe or creating a custom solution, having an expert team of developers on hand can make all the difference.
Downtime, or even simple mistakes that affect user experience, can be enough to lead to a loss in sales.
To find out if Trio’s developers can assist you, request a consult.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does a payment gateway work?
A payment gateway works by encrypting your customer’s payment details and routing them securely through the payment processor to the customer’s bank for authorization, then back to your platform with an approval or decline, all within a few seconds.
What is the difference between a payment gateway and a payment processor?
The difference between a payment gateway and a payment processor comes down to function. The gateway captures and encrypts the payment data, while the processor actually moves the funds between the customer’s bank and your merchant account.
How much does it cost to integrate a payment gateway?
Payment gateway integration costs vary widely depending on the method you choose, with hosted solutions carrying lower upfront development costs but ongoing transaction fees. Custom builds require significant developer time and compliance investment before you process a single transaction.
How long does payment gateway integration take?
Payment gateway integration timelines depend on the complexity of your setup. A hosted gateway with a pre-built SDK can go live in days, while a fully custom or API-based integration with ERP and CRM connections may take several weeks to build, test, and deploy safely.
Do I need a merchant account to accept payments online?
Yes, you need a merchant account to accept payments online, as a merchant account acts as the holding account where approved funds sit before they transfer to your business bank account, and most payment gateway providers either require one or bundle it into their service to simplify setup.
Is it safe to integrate a third-party payment gateway?
Integrating a reputable third-party payment gateway is generally safer than building your own payment handling, because established providers maintain PCI DSS certification, invest heavily in fraud detection, and carry responsibility for the security of data within their system.
What happens if a payment gateway goes down?
If a payment gateway goes down, transactions cannot process, which means lost revenue and a poor customer experience. This risk is one reason why larger businesses integrate multiple gateway providers as fallbacks.