Digital banks are incredibly popular. Roughly 80% of millennials prefer to bank digitally.
This has meant that global regulations have had to shift to accommodate both online banking and traditional banking, and financial institutions have had to adapt in order to ensure compliance.
If you are in the fintech sector, providing banking services online, you need to ensure you are aware of all the different laws and regulations of your jurisdiction, and that you are ready to make alterations to your digital banking solution to adapt to any future changes.
Failing to do so will result in fines, revoked licenses, and irreparable damage to your reputation.
So, now that you understand why regulatory requirements for digital banks are critical, what does it encompass?
At the moment, the core regulatory requirements for digital banks include:
- KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML (Anti-Money Laundering)
- Capital Requirements and Risk Management
- Data Privacy and Cybersecurity Compliance
- Licensing and Regulatory Approvals
- Reporting and Auditing Standards
Let’s look at these in more detail so that you understand all the requirements to keep your digital financial system compliant.
At Trio, we provide industry-experienced developers who are familiar with all the requirements of regulatory compliance in banking and fintech, and can integrate these considerations into your app from the ground up.
Our staff augmentation model means you connect with developers quickly, getting your code done faster than you could through traditional hiring models.
What Is a Digital Bank?
A digital bank, as the name suggests, works primarily online. Digital banking’s main advantage to companies is that they don’t need a physical location and don’t have the associated costs.
Digital banks can also make use of the latest technology to expand their offerings, sometimes even using third-party integrations to offer their clients exactly what they need while prioritizing the overall customer experience.
In some cases, a digital bank can be a service offered by an existing bank, but it can also be an independent neobanks that make use of its own licensing or banking as a service (BaaS).
Why Regulation Matters in Digital Banking
Digital banks handle large quantities of customer data, including delicate personal information and their actual money. Strong regulations are designed to keep users safe. Digital banking compliance gives them access to the necessary certifications required to operate, but also helps build user trust.
Balancing Innovation and Compliance
One of the many reasons people like to use online financial services is because of their new, innovative features. However, in order to prevent financial crime, digital banks must balance innovation and compliance.
The best way to do this is to integrate existing banking laws and regulations into your development pipelines. An experienced fintech developer will be able to do this with ease.
It is also important to use techniques like modular coding, which increase your code’s flexibility, allowing you to make changes later on based on shifting requirements.
Trust, Security, and Consumer Protection
Not managing sensitive data correctly causes users to lose trust in you.
You don’t want any damage to your reputation in an industry where you need to deal with people’s money and retain customer loyalty.
Being able to advertise the efforts you are putting into regulatory frameworks can play a massive role in your advertising, as well as in your collaborations with other vendors.
Obviously, these laws help you keep the risk of any actual security breaches, as well as other problems like money laundering or terrorist financing.
Core Regulatory Requirements for Digital Banks
We’ve mentioned regulatory requirements several times, but what exactly is regulated? Where do these compliance measures apply?
KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML (Anti-Money Laundering)
These regulations are generally related to strong customer authentication, ensuring the right people are using the application instead of impostors, as well as anti-money laundering and other anti terrorism financing mechanisms.
Some potential requirements include customer due diligence (CDD), transaction monitoring, and reporting of any suspicious activities.
Capital Requirements and Risk Management
Minimum capital requirements can be very difficult to meet as a startup without many banking customers. A part of this is to facilitate risk management frameworks that protect the people who deposit currency and ensure solvency.
Risk assessment and other risk-based analyses only help to a degree. You need capital adequacy to provide the necessary liquidity to cover those risks if they occur. Liquidity coverage ratios are a common regulatory requirement.
Data Privacy and Cybersecurity Compliance
There are a variety of regulations related to data privacy and cybersecurity. These differ regionally (which we’ll cover more below), but the most impactful examples include GDPR in Europe or CCPA in California. These regulations control the way companies handle data.
Digital banks are required to secure customer data, obtain consent for things like data processing and ongoing transaction monitoring, and implement robust cybersecurity protocols to make sure there are no unauthorized users accessing the wrong accounts or any other security breaches.
Licensing and Regulatory Approvals
You need to prove that your product is secure and that you prioritize ethical user data handling in order to get licenses from regulatory authorities. These are requirements to offer your services legally.
To obtain these, the processes differ greatly, but usually require submitting a business plan, demonstrating capital adequacy, and showing how you have prepared your code and what practices you have put in place.
Reporting and Auditing Standards
Obtaining a licence isn’t the end of the process. To keep these licences, you need to implement regular reporting on financial performance, operational risk, and compliance status.
There is a focus on transparency, especially when it comes to suspicious transactions, capital reserves, and customer complaints.
Global Regulatory Frameworks and Market Differences
As mentioned, different regions have different regulations. It would be impossible to cover everything, but we can look at some of the most popular examples.
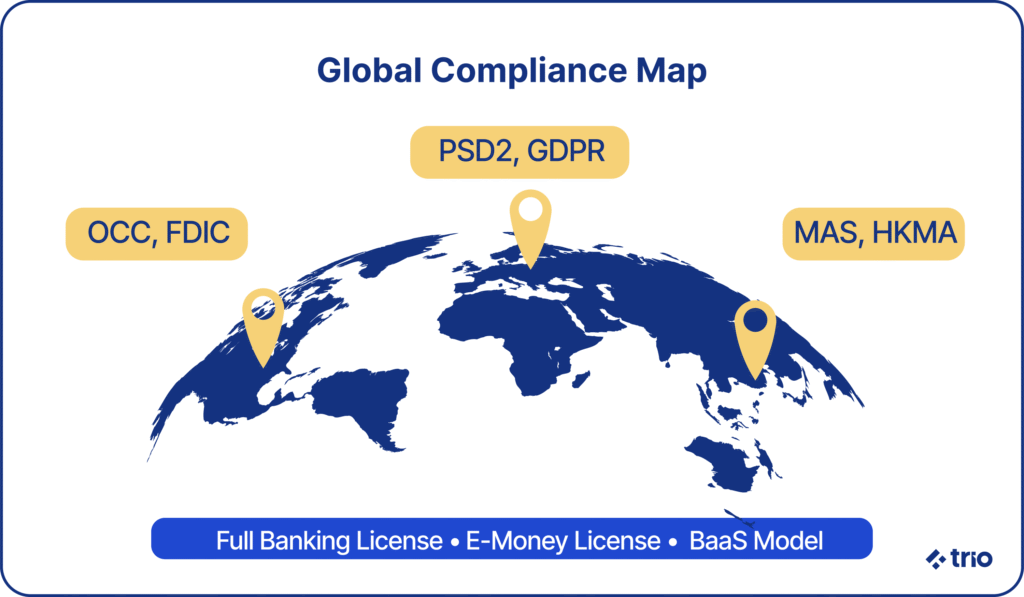
- U.S.: OCC, FDIC, and State-Level Compliance
- Europe: PSD2, EBA Guidelines, and GDPR
- Asia-Pacific: MAS (Singapore), HKMA (Hong Kong), etc.
Licensing Approaches: A Comparative Look
There are some different ways to approach licensing. The most popular examples include full banking licences and E-money institution licenses.
A full banking licence lets your digital bank accept deposits and offer credit services, while an e-money license lets you use payment processing and provide digital wallets, but restricts your lending abilities. The choice depends on your long-term strategy.
You could also use Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS), where you make use of another institution’s license and simply provide the digital platform. While this lowers the barrier to entry, regulators are starting to evaluate these models more closely to ensure customer protection is always prioritized.
Compliance Challenges for Digital Banks
We’ve already mentioned how it can be difficult to balance innovation and evolving regulations. You need to ensure current compliance, while being incredibly agile, not only to be able to grow your own services, but also to be able to adapt quickly to regulatory changes.
While technology plays a big role in this, developing an agile team is critical.
Constant shifting of compliance regulations and differences between regions can also become expensive. You need legal expertise, constant system updates, staff training, new code, and a variety of other measures that all cost money.
Expanding is difficult even without the financial considerations. There are challenges related to data localization, jurisdictional licensing, and taxes. Providing the same digital banking app to people all over the world, with a consistent user experience, while still accounting for these differences, requires incredible skill.
Technology’s Role in Regulatory Compliance
Technology has played a big part in changing the way we look at regulations. It has been both a catalyst and a solution.
Regulatory Technology (RegTech) has allowed digital banks to automate processes like KYC/AML. By using AI capabilities, they have also been able to monitor real-time transactions, generate audit trails without any manual intervention, and remove the possibility of human error.
Modern platforms also facilitate data aggregation for more complete reporting, automated alerts, and even user-friendly dashboards that make it easy to identify trends and issues.
However, we cannot ignore the fact that compliance must be a part of the entire software development lifecycle to ensure you are compliant from inception and can minimize retroactive fixes and any delays.
Best Practices for Staying Compliant
Several best practices can assist fintech companies with keeping their digital offerings compliant. Doing your due diligence is critical to prevent issues.
First, build a tech team made up of developers who are familiar with the regulations of the financial services industry, just like the kind available at Trio. These developers should be well-trained on everything from data protection and encryption to transaction transparency.
It is also best to monitor your compliance continuously with periodic audits and by tracking the relevant KPIs.
Working directly with regulators will ensure you understand what is needed from you. There are a variety of options out there designed for startups, scaleups, and enterprises, respectively.
The Future of Regulatory Compliance in Digital Banking
While it is impossible to predict what laws will be passed by regulatory bodies in the future, we can stay informed on current trends in order to identify areas where compliance and regulatory reporting may change.
AI systems are allowing many different service providers to automate their data analysis and make inferences more accurately. In the world of digital banking, there is no reason people won’t try to use these tools for risk analysis, real-time compliance checks, and smarter fraud detection.
However, this brings about additional issues with data protection, which may lead to new regulatory processes.
A couple of firms are also experimenting with decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols. Regulators are going to need new frameworks for accountability in this field to address issues related to money laundering and terrorist financing.
We’ve noticed that open banking and API security standards are also being discussed, thanks to the increased access APIs provide to financial data. The way we access third-party services may have to be revised.
Trio’s focus on a single niche, instead of more generalized development, allows our developers to stay on top of industry trends like these. They can advise you on the best way to set up your digital bank for both current and future regulatory compliance.
If you need developers to expand your team rapidly, you need to make changes to your products quickly without sacrificing quality or compliance, and you are in the right place.
We can connect you with developers in as little as 24 hours, with a 97% success rate. Reach out to us to schedule a free consultation.